Hypoglycemia is an abnormally low level of sugar in the blood. It is the body’s inability to properly handle large amounts of sugar that the average person consumes. In hypoglycemia, the pancreas sends out too much insulin and the blood sugar plummets below the level necessary to maintain well-being.
What are the symptoms?Common symptoms of hypoglycemia include: excessive sweating, tremors, dizziness, unconscious state and seizures. In rare cases, the BP can go very high and in a diabetic with pre-existing coronary artery disease, it can even cause a heart attack.
What are the causes?
Low blood sugar is often caused due to the mismatch between the food consumed and the anti-diabetic medicine the patient is taking. It can also be a result of skipping a meal after taking the diabetic medicine or having too little food because of fever, loose motions etc after taking the regular anti-diabetic medicines.
What is the treatment?
The immediate treatment is to give the patient glucose or sugar to increase the blood sugar level after checking it either by a glaucometer, if there is one present at home or from the nearest laboratory.
What is hyperglycemia?
It is a condition where a person’s blood contains an abnormally high level of blood sugar (glucose). Chronic levels, exceeding 125 mg/dl can cause organ damage. When the body has too little, or not enough insulin or when the body can’t use insulin properly, it leads to high blood glucose.
What are the symptoms?
High blood sugar is also known as hyperglycemia. The symptoms of hyperglycemia include: Polyuria (excessive urination), Polydipsia (excessive thirst), Polyphagia (excessive appetite), weight loss, blurring of vision and delayed wound healing.
What are the causes?Various factors that contribute to hyperglycemia are: skipping or forgetting your insulin or oral glucose-lowering medicine, intake of excessive carbohydrates and calories, infection, increased stress, decreased activity or exercising less than usual, strenuous physical activity etc.
What is the treatment?Hyperglycemia is treated with oral anti-diabetic drugs and/or insulin depending upon the condition of the patient.
What does the doctor say?
Both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are conditions that are detrimental to one’s health. They require immediate attention from a qualified specialist.
Prof Dr CV Harinarayan, MD (Int Med), DM (Endocrinology, AIIMS, New Delhi), chief consultant, Wockhardt Hospitals![submenu-img]() Ramesh Awasthi: Kanpur's 'Karma Yogi' - Know inspirational journey of 'common man' devoted for society
Ramesh Awasthi: Kanpur's 'Karma Yogi' - Know inspirational journey of 'common man' devoted for society![submenu-img]() Tovino Thomas accused of stopping his film Vazhakku's release by director Sanal Kumar Sasidharan: 'The agenda of...'
Tovino Thomas accused of stopping his film Vazhakku's release by director Sanal Kumar Sasidharan: 'The agenda of...'![submenu-img]() PM Modi wears turban, serves langar at Gurudwara Patna Sahib in Bihar, watch
PM Modi wears turban, serves langar at Gurudwara Patna Sahib in Bihar, watch![submenu-img]() Anil Ambani’s debt-ridden Reliance’s ‘buyer’ now waits for RBI nod, wants Rs 80000000000…
Anil Ambani’s debt-ridden Reliance’s ‘buyer’ now waits for RBI nod, wants Rs 80000000000…![submenu-img]() Man in bizarre jeans dances to Tinku Jiya in crowded metro, viral video makes internet furious
Man in bizarre jeans dances to Tinku Jiya in crowded metro, viral video makes internet furious![submenu-img]() Maharashtra Board HSC, SSC Results 2024: MSBSHSE class 10, 12 results soon at mahresult.nic.in, latest update here
Maharashtra Board HSC, SSC Results 2024: MSBSHSE class 10, 12 results soon at mahresult.nic.in, latest update here![submenu-img]() Meet IIT-JEE topper who passed JEE Advanced with AIR 1, decided to drop out of IIT due to…
Meet IIT-JEE topper who passed JEE Advanced with AIR 1, decided to drop out of IIT due to…![submenu-img]() Meet IPS Idashisha Nongrang, who became Meghalaya's first woman DGP
Meet IPS Idashisha Nongrang, who became Meghalaya's first woman DGP![submenu-img]() CBSE Results 2024: CBSE Class 10, 12 results date awaited, check latest update here
CBSE Results 2024: CBSE Class 10, 12 results date awaited, check latest update here![submenu-img]() Meet man, who was denied admission in IIT due to blindness, inspiration behind Rajkummar Rao’s film, now owns...
Meet man, who was denied admission in IIT due to blindness, inspiration behind Rajkummar Rao’s film, now owns...![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'
DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message
DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here
DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar
DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth
DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth![submenu-img]() Remember Harsh Lunia? Just Mohabbat child star, here's how former actor looks now, his wife is Bollywood's popular...
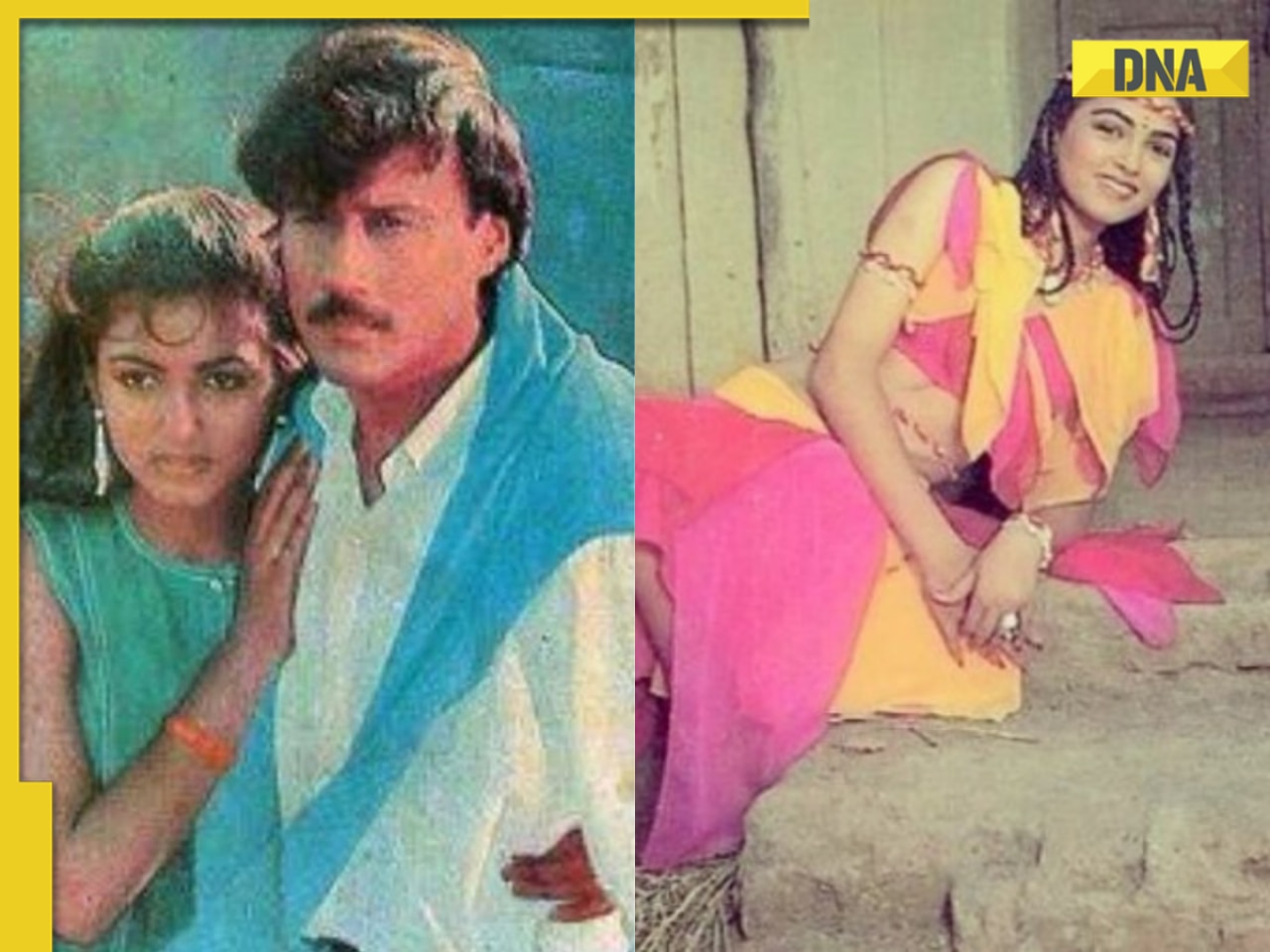
Remember Harsh Lunia? Just Mohabbat child star, here's how former actor looks now, his wife is Bollywood's popular...![submenu-img]() Mother's Day 2024: Bollywood supermoms who balance motherhood, acting, and run multi-crore businesses
Mother's Day 2024: Bollywood supermoms who balance motherhood, acting, and run multi-crore businesses![submenu-img]() Rocky Aur Rani's Golu aka Anjali Anand shocks fans with drastic weight loss without gym, says fitness secret is...
Rocky Aur Rani's Golu aka Anjali Anand shocks fans with drastic weight loss without gym, says fitness secret is...![submenu-img]() In pics: Ram Charan gets mobbed by fans during his visit to Pithapuram for ‘indirect campaign’ for uncle Pawan Kalyan
In pics: Ram Charan gets mobbed by fans during his visit to Pithapuram for ‘indirect campaign’ for uncle Pawan Kalyan![submenu-img]() Streaming This Week: Yodha, Aavesham, Murder In Mahim, Undekhi season 3, latest OTT releases to binge-watch
Streaming This Week: Yodha, Aavesham, Murder In Mahim, Undekhi season 3, latest OTT releases to binge-watch![submenu-img]() Haryana Political Crisis: Will 3 independent MLAs support withdrawal impact the present Nayab Saini led-BJP government?
Haryana Political Crisis: Will 3 independent MLAs support withdrawal impact the present Nayab Saini led-BJP government?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: Why Harvey Weinstein's rape conviction was overturned, will beleaguered Hollywood mogul get out of jail?
DNA Explainer: Why Harvey Weinstein's rape conviction was overturned, will beleaguered Hollywood mogul get out of jail?![submenu-img]() What is inheritance tax?
What is inheritance tax?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is cloud seeding which is blamed for wreaking havoc in Dubai?
DNA Explainer: What is cloud seeding which is blamed for wreaking havoc in Dubai?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?
DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?![submenu-img]() Tovino Thomas accused of stopping his film Vazhakku's release by director Sanal Kumar Sasidharan: 'The agenda of...'
Tovino Thomas accused of stopping his film Vazhakku's release by director Sanal Kumar Sasidharan: 'The agenda of...'![submenu-img]() Ratna Pathak Shah calls Guru Dutt and Bimal Roy's films 'offensive', says, 'women are constantly...'
Ratna Pathak Shah calls Guru Dutt and Bimal Roy's films 'offensive', says, 'women are constantly...'![submenu-img]() Shreyas Talpade recalls how he felt bad when his film Kaun Pravin Tambe did not release in theatres: 'It deserved...'
Shreyas Talpade recalls how he felt bad when his film Kaun Pravin Tambe did not release in theatres: 'It deserved...'![submenu-img]() Anup Soni slams his deepfake video from Crime Patrol, being used to promote IPL betting
Anup Soni slams his deepfake video from Crime Patrol, being used to promote IPL betting![submenu-img]() Real story that inspired Heeramandi: The tawaif who helped Gandhi fight British Raj, was raped, abused, died in...
Real story that inspired Heeramandi: The tawaif who helped Gandhi fight British Raj, was raped, abused, died in...![submenu-img]() Man in bizarre jeans dances to Tinku Jiya in crowded metro, viral video makes internet furious
Man in bizarre jeans dances to Tinku Jiya in crowded metro, viral video makes internet furious![submenu-img]() Lift collides with roof in Noida society after brakes fail, 3 injured
Lift collides with roof in Noida society after brakes fail, 3 injured![submenu-img]() Zomato CEO Deepinder Goyal invites employees' moms to office for Mother's Day celebration, watch
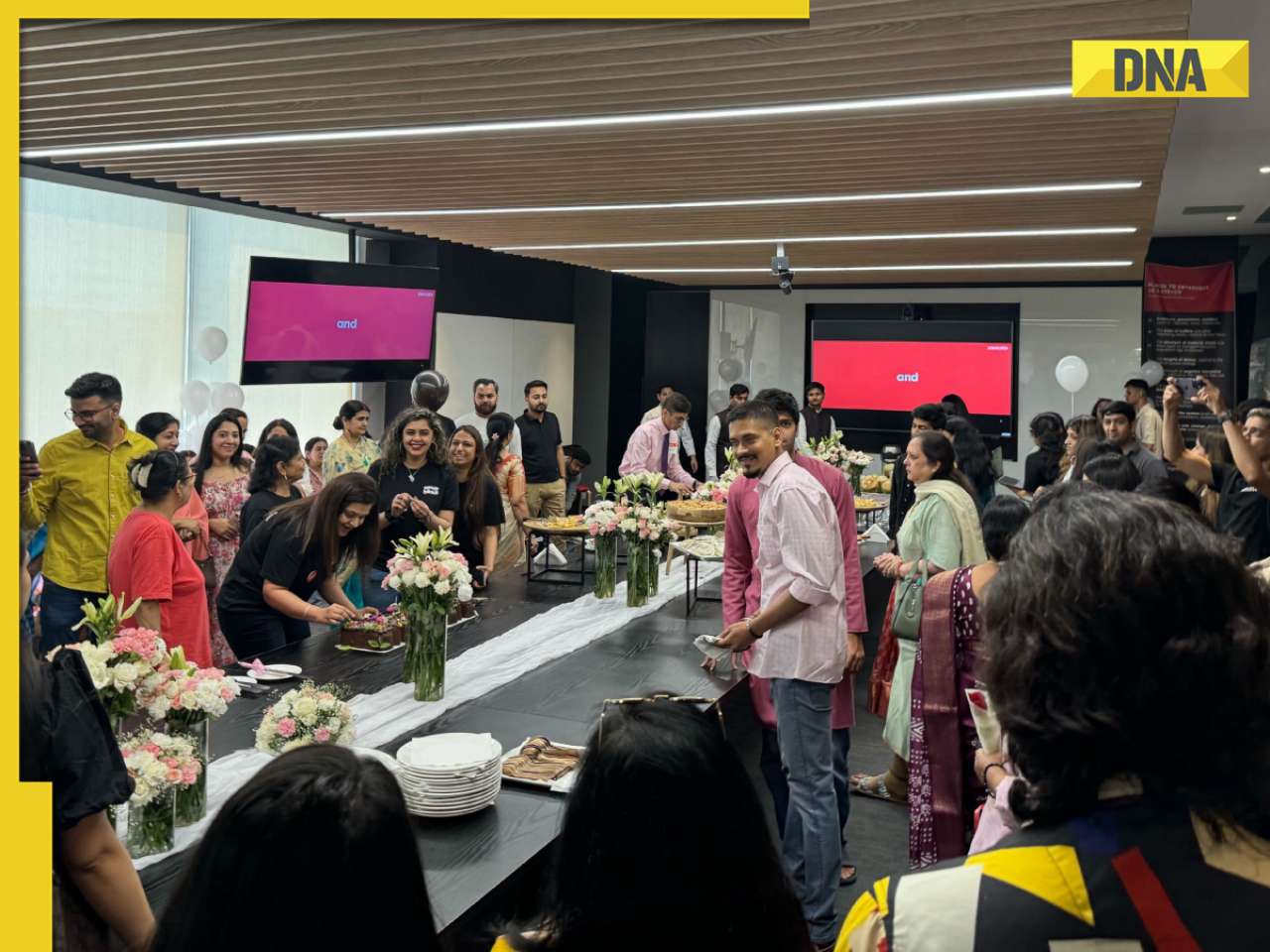
Zomato CEO Deepinder Goyal invites employees' moms to office for Mother's Day celebration, watch![submenu-img]() This clip of kind woman feeding rotis to stray cows will bring tears of joy to your eyes, watch
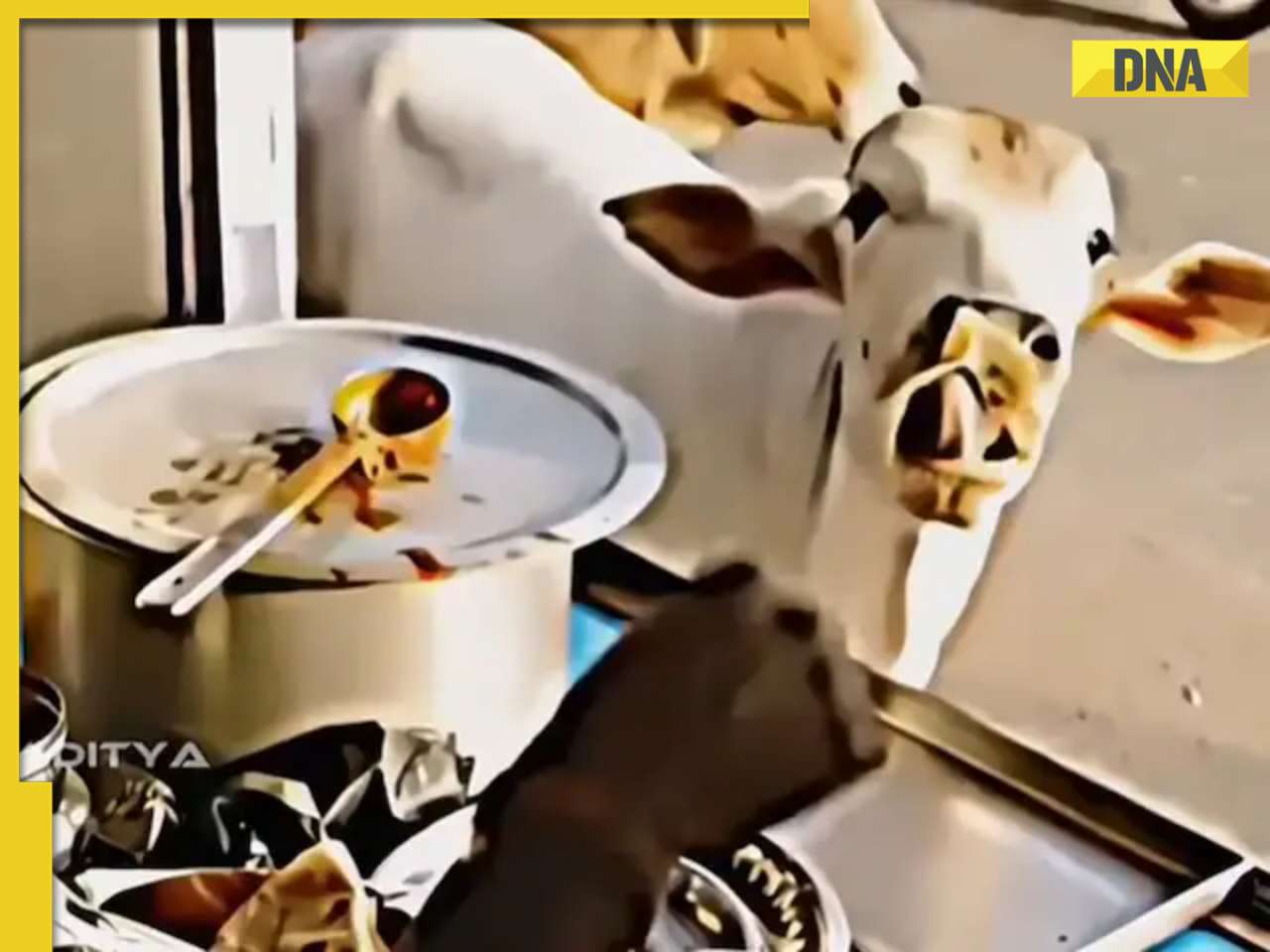
This clip of kind woman feeding rotis to stray cows will bring tears of joy to your eyes, watch![submenu-img]() Viral video: Seagull swallows squirrel whole in single go, internet is stunned
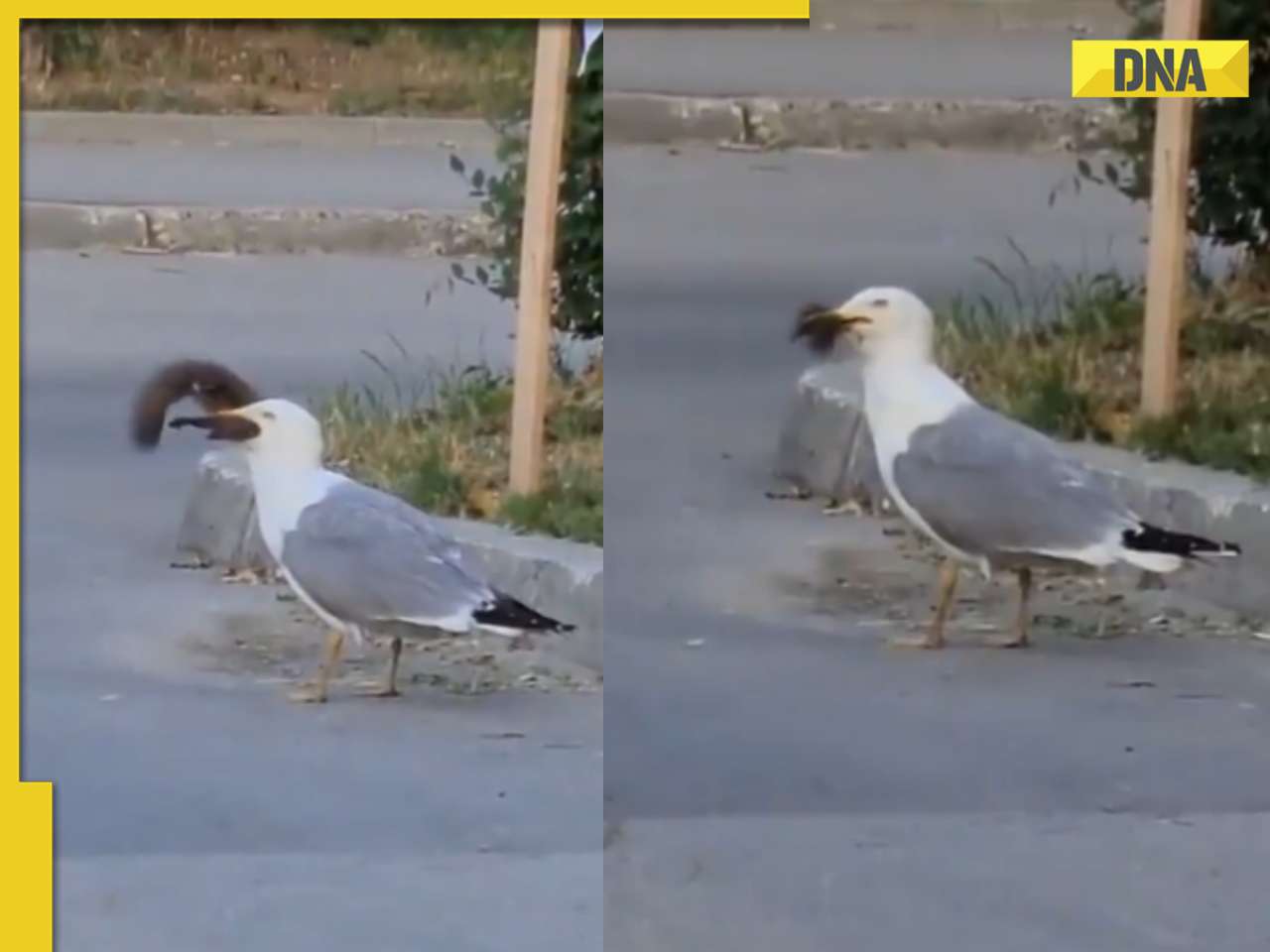
Viral video: Seagull swallows squirrel whole in single go, internet is stunned




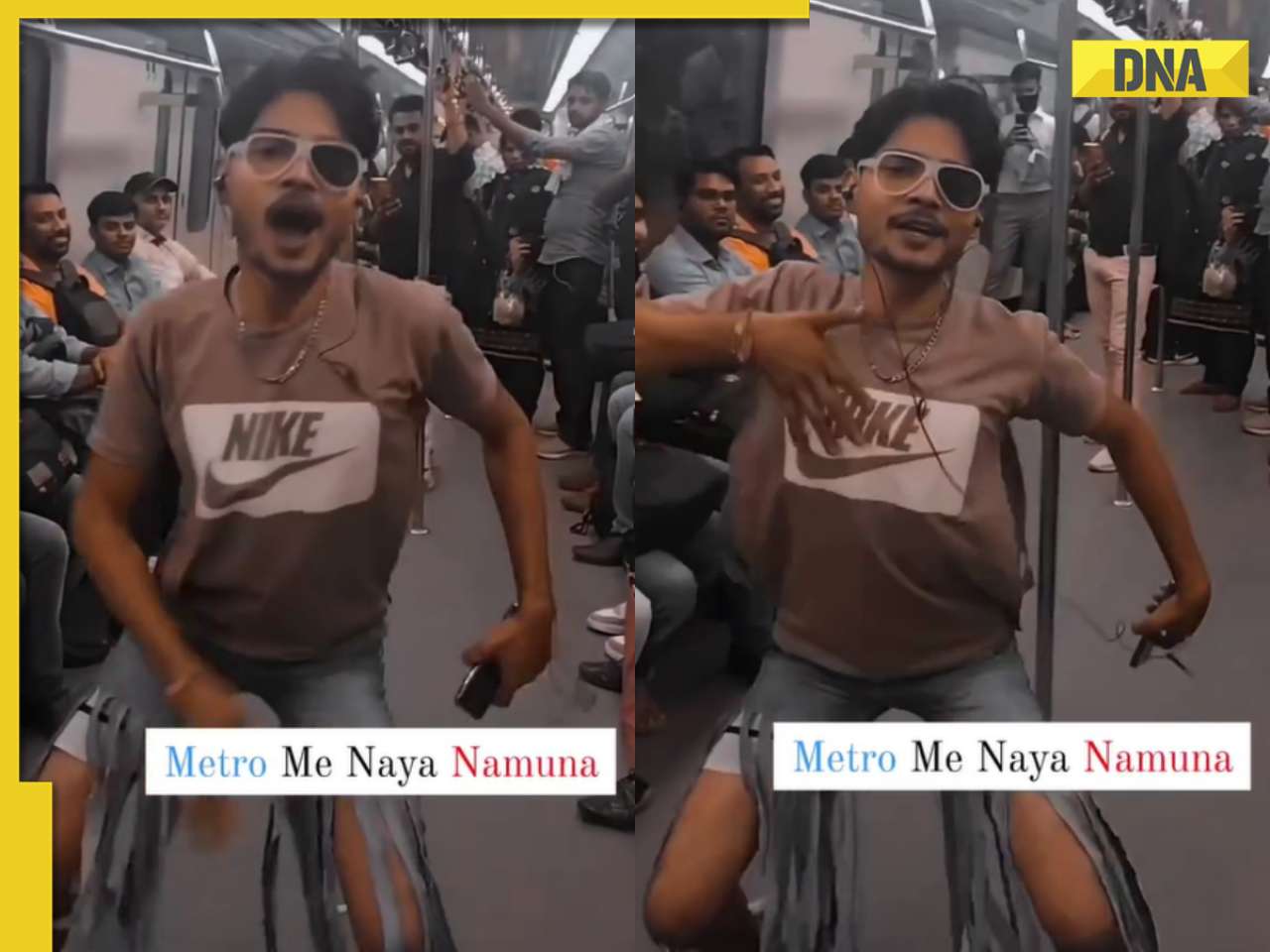




















































)
)
)
)
)
)