Fixed maturity plans (FMP) floated by mutual funds requires a thorough due diligence process on the part of the investor before committing any money to the plans.
Fixed maturity plans (FMP) floated by mutual funds requires a thorough due diligence process on the part of the investor before committing any money to the plans. This article takes you through the due diligence process for investing in FMPs.
What are fixed maturity plans?
Fixed maturity plans are investment schemes floated by mutual funds and are close-ended with a maturity period ranging from three months to five years. These plans are predominantly debt-oriented, while some of them may have a small equity component.
The objective of such a scheme is to generate steady returns over a fixed-maturity period and immunising the investor against market fluctuations.
How do FMPs work?
FMPs are typically passively managed fixed-income schemes with the fund manager locking into investments with maturities corresponding with the maturity of the plan.
The objective is to lock into a certain rate of return on the assets at inception, thereby protecting the schemes against market fluctuations. Unless specified in the objective of a
FMP, investments are in risk- free or highly-rated assets for principal protection. FMPs with equity component will be more dynamically managed as fund managers cannot invest in equities for locking in to inception returns.
Factors influencing decision to invest in a FMP
The following are the key factors which an investor must look at before investing in FMPs.
1. Cash flow forecasting: FMPs are suitable for investors who require locking in funds for a particular period of time. E.g. If an individual has a certain cash outflow in three years time, investing in a debt FMP with three year maturity can be considered as the investor is only concerned with receiving the principal plus return on the investment at the end of three years.
2. Immunisation of investments: FMPs are a good investment vehicle for investors who are targeting a return on their investments over a fixed period of time and are indifferent to market volatility within that period.
3. Interest rates currently prevailing in the market: The investor should look at interest rates on government bonds, corporate bonds, commercial papers, certificate of deposits, securitised assets, bank deposits, company deposits and other short to medium term fixed income products before taking an investment decision in a FMP. This exercise will give an idea to the investor on the return one can expect on FMPs.
The investor can then use this knowledge to lock into returns through FMPs or directly through other fixed income products.
4. Kinks in the curve: The yield curve sometimes exhibit varying forms against the normal upward sloping nature of the curve. In cases where the yield curve is inverted with short term rates higher than long term rates, investors can look for opportunities to capture the deviation through FMP's.
5. View on the equity market: FMPs are generally meant for investors who are indifferent to market fluctuations in the short term. However it pays to form a view on the markets for investing in FMPs with equity components as equities markets carry a higher risk in the short term than in the long term.
Risks in FMPs
The close ended nature of FMPs do not really protect them against risks including market, credit and liquidity risks. FMPs have the potential for capital depreciation. Investors should take a closer look at the risks in FMPs before making an investment decision. The risks in FMPs are elaborated below.
1. Market risk: Market risk in an FMP is high where there is an equity component in the plan. The fixed maturity nature of the FMP, forces the fund manager to take shorter term calls on equities. This can lead to trading losses as the fund manager does not have the luxury of time to hold on to the investments.
2. Interest rate risk: FMPs are designed to immunise investor against interest rate risk. However, as a plan is launched and money is collected, interest rates can fall before the money is invested and the funds will have to be invested at a lower rate. The non availability of a forward rate market in India is a chief contributor to interest rate risk in a FMP.
3. Gapping risk: If the fund manager is unable to find assets exactly maturing with the plan, this leads to a risk of asset liability mismatch. This risk can negate the immunisation of the investment.
4. Credit risk: The credit portfolio in the plan can suffer in case of downgrades by rating agencies. Downgrades bring down the price of the securities as investors demand a higher risk premium on the asset leading to higher credit spreads. If the fund manager is forced to liquidate the security if it crosses a threshold rating levels, the scheme will suffer capital loss.
5. Terms for large investors: Investors will have to watch out for terms on large investors i.e., if large investors are given zero or low exit loads.
This can lead to early exit by large investors from the plan. This will affect the returns on the plan substantially.
Carrying out the above suggested due diligence on a FMP can protect investors from heart aches on wrong decision on FMP investments. FMPs are illiquid and investments can be only liquidated in specific periods. During periods where redemption is allowed, markets may have moved adversely leading to capital loss on liquidation. The load barriers are also quite heavy to prevent pre-mature withdrawals.
![submenu-img]() Balancing Risk and Reward: Tips and Tricks for Good Mobile Trading
Balancing Risk and Reward: Tips and Tricks for Good Mobile Trading![submenu-img]() Balmorex Pro [Is It Safe?] Real Customers Expose Hidden Dangers
Balmorex Pro [Is It Safe?] Real Customers Expose Hidden Dangers![submenu-img]() Sight Care Reviews (Real User EXPERIENCE) Ingredients, Benefits, And Side Effects Of Vision Support Formula Revealed!
Sight Care Reviews (Real User EXPERIENCE) Ingredients, Benefits, And Side Effects Of Vision Support Formula Revealed!![submenu-img]() Java Burn Reviews (Weight Loss Supplement) Real Ingredients, Benefits, Risks, And Honest Customer Reviews
Java Burn Reviews (Weight Loss Supplement) Real Ingredients, Benefits, Risks, And Honest Customer Reviews![submenu-img]() Gurucharan Singh is still unreachable after returning home, says Taarak Mehta producer Asit Modi: 'I have been trying..'
Gurucharan Singh is still unreachable after returning home, says Taarak Mehta producer Asit Modi: 'I have been trying..'![submenu-img]() RBSE 12th Result 2024 Live Updates: Rajasthan Board Class 12 results DECLARED, get direct link here
RBSE 12th Result 2024 Live Updates: Rajasthan Board Class 12 results DECLARED, get direct link here![submenu-img]() IIT graduate Indian genius ‘solved’ 161-year old maths mystery, left teaching to become CEO of…
IIT graduate Indian genius ‘solved’ 161-year old maths mystery, left teaching to become CEO of…![submenu-img]() RBSE 12th Result 2024 Live Updates: Rajasthan Board Class 12 results to be announced soon, get direct link here
RBSE 12th Result 2024 Live Updates: Rajasthan Board Class 12 results to be announced soon, get direct link here![submenu-img]() Meet doctor who cracked UPSC exam to become IAS officer but resigned after few years due to...
Meet doctor who cracked UPSC exam to become IAS officer but resigned after few years due to...![submenu-img]() IIT graduate gets job with Rs 45 crore salary package, fired after few years, buys Narayana Murthy’s…
IIT graduate gets job with Rs 45 crore salary package, fired after few years, buys Narayana Murthy’s…![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'
DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message
DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here
DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar
DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth
DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth![submenu-img]() Urvashi Rautela mesmerises in blue celestial gown, her dancing fish necklace steals the limelight at Cannes 2024
Urvashi Rautela mesmerises in blue celestial gown, her dancing fish necklace steals the limelight at Cannes 2024![submenu-img]() Kiara Advani attends Women In Cinema Gala in dramatic ensemble, netizens say 'who designs these hideous dresses'
Kiara Advani attends Women In Cinema Gala in dramatic ensemble, netizens say 'who designs these hideous dresses'![submenu-img]() Influencer Diipa Büller-Khosla looks 'drop dead gorgeous' in metallic structured dress at Cannes 2024
Influencer Diipa Büller-Khosla looks 'drop dead gorgeous' in metallic structured dress at Cannes 2024![submenu-img]() Kiara Advani stuns in Prabal Gurung thigh-high slit gown for her Cannes debut, poses by the French Riviera
Kiara Advani stuns in Prabal Gurung thigh-high slit gown for her Cannes debut, poses by the French Riviera![submenu-img]() Heeramandi star Taha Shah Badussha makes dashing debut at Cannes Film Festival, fans call him ‘international crush’
Heeramandi star Taha Shah Badussha makes dashing debut at Cannes Film Festival, fans call him ‘international crush’![submenu-img]() Haryana Political Crisis: Will 3 independent MLAs support withdrawal impact the present Nayab Saini led-BJP government?
Haryana Political Crisis: Will 3 independent MLAs support withdrawal impact the present Nayab Saini led-BJP government?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: Why Harvey Weinstein's rape conviction was overturned, will beleaguered Hollywood mogul get out of jail?
DNA Explainer: Why Harvey Weinstein's rape conviction was overturned, will beleaguered Hollywood mogul get out of jail?![submenu-img]() What is inheritance tax?
What is inheritance tax?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is cloud seeding which is blamed for wreaking havoc in Dubai?
DNA Explainer: What is cloud seeding which is blamed for wreaking havoc in Dubai?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?
DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?![submenu-img]() Gurucharan Singh is still unreachable after returning home, says Taarak Mehta producer Asit Modi: 'I have been trying..'
Gurucharan Singh is still unreachable after returning home, says Taarak Mehta producer Asit Modi: 'I have been trying..'![submenu-img]() ‘Jo mujhse bulwana chahte ho…’: Angry Dharmendra lashes out after casting his vote in Lok Sabha Elections 2024
‘Jo mujhse bulwana chahte ho…’: Angry Dharmendra lashes out after casting his vote in Lok Sabha Elections 2024![submenu-img]() Deepika Padukone spotted with her baby bump as she steps out with Ranveer Singh to cast her vote in Lok Sabha elections
Deepika Padukone spotted with her baby bump as she steps out with Ranveer Singh to cast her vote in Lok Sabha elections![submenu-img]() Jr NTR surprises fans on birthday, announces NTR 31 with Prashanth Neel, shares details
Jr NTR surprises fans on birthday, announces NTR 31 with Prashanth Neel, shares details ![submenu-img]() 86-year-old Shubha Khote wins hearts by coming out to cast her vote in Lok Sabha elections, says meant to inspire voters
86-year-old Shubha Khote wins hearts by coming out to cast her vote in Lok Sabha elections, says meant to inspire voters![submenu-img]() Watch viral video: Man gets attacked after trying to touch ‘pet’ cheetah; netizens react
Watch viral video: Man gets attacked after trying to touch ‘pet’ cheetah; netizens react![submenu-img]() Real story of Lahore's Heermandi that inspired Netflix series
Real story of Lahore's Heermandi that inspired Netflix series![submenu-img]() 12-year-old Bengaluru girl undergoes surgery after eating 'smoky paan', details inside
12-year-old Bengaluru girl undergoes surgery after eating 'smoky paan', details inside![submenu-img]() Viral video: Pakistani man tries to get close with tiger and this happens next
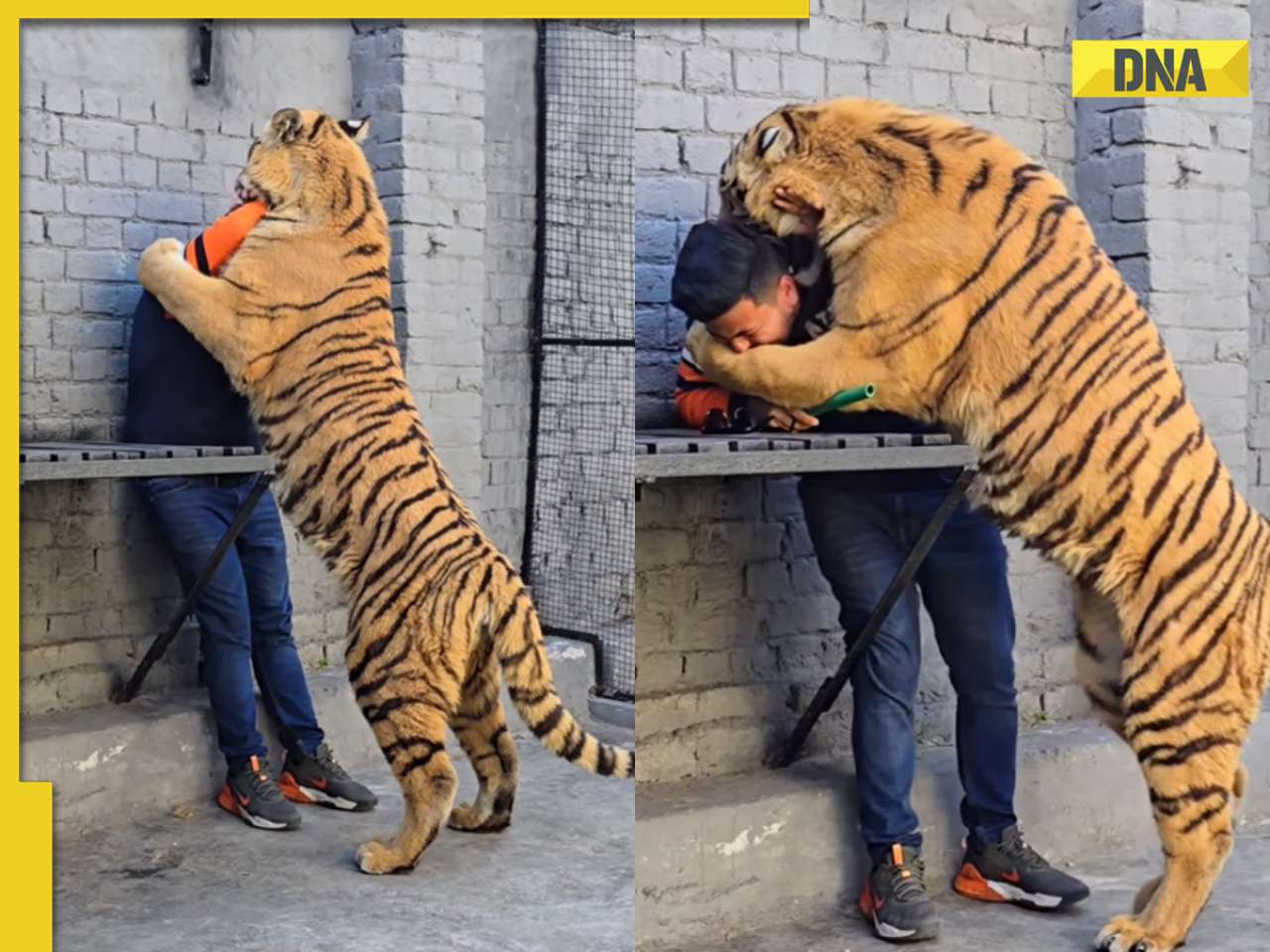
Viral video: Pakistani man tries to get close with tiger and this happens next![submenu-img]() Owl swallows snake in one go, viral video shocks internet
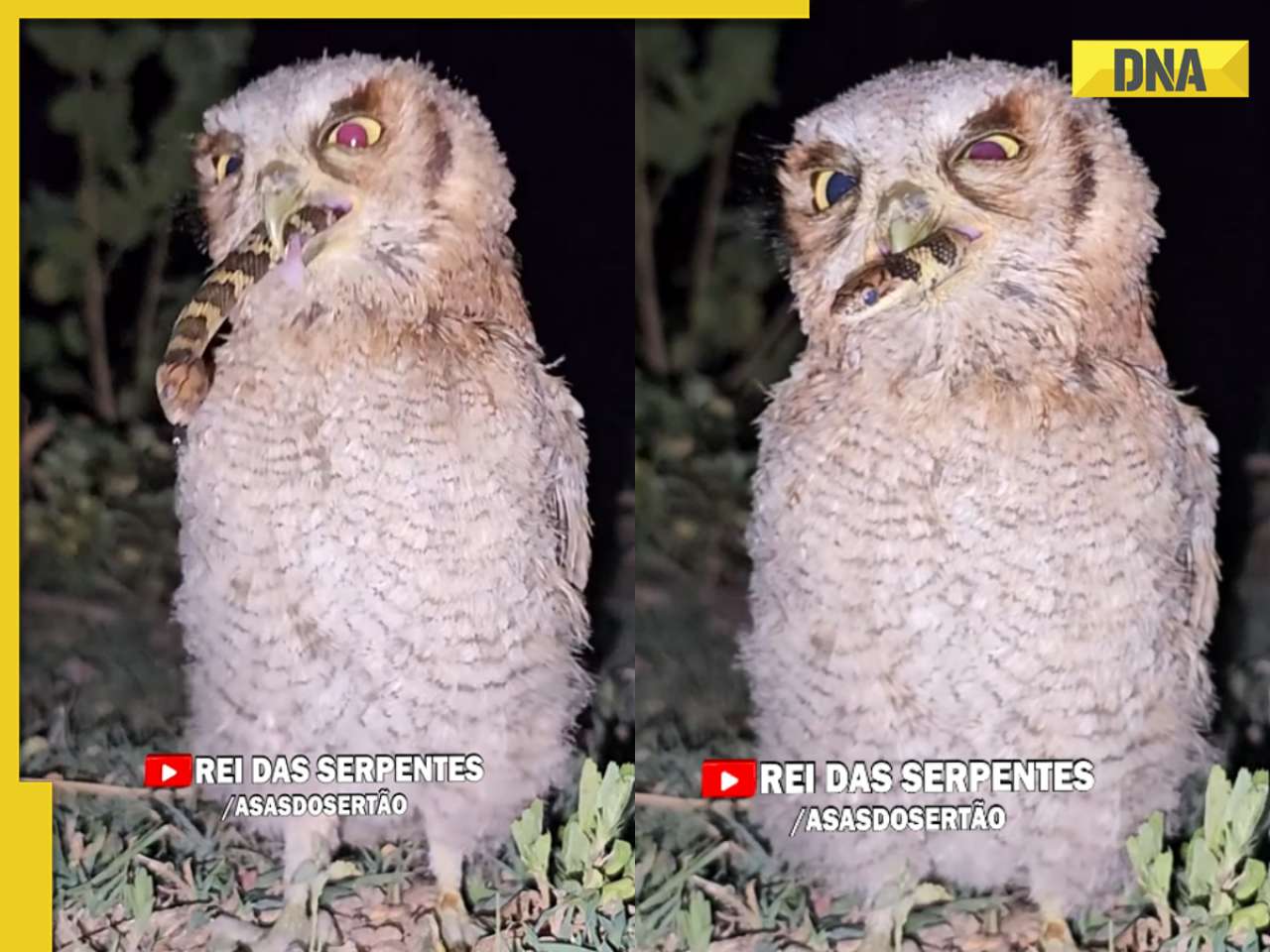
Owl swallows snake in one go, viral video shocks internet























































)
)
)
)
)
)