Here is a summary of the proposals his government made, based on a letter he sent to European Commission chief Jean-Claude Juncker on Monday.
Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras flew to Brussels to meet Greece's international creditors on Wednesday to try to bridge gaps on key elements of the proposals made by his left-wing government to shore up state finances in
return for vital loans.
Here is a summary of the proposals his government made, based on a letter he sent to European Commission chief Jean-Claude Juncker on Monday.
PENSIONS
Extra savings on pensions worth 1.05 percent of GDP in 2016 and 1.1 percent in 2017, with measures including an increase in pension contributions and higher healthcare contributions for pensioners.
Early retirement to be curbed gradually from 2016 to reach a retirement age of 67 for all by 2025, but some exemptions to be maintained, including for arduous professions and mothers with disabled children.
A special benefit for some low-income pensioners, amounting to between 57 and 230 euros ($65 and $261) a month, to remain for now but be replaced from 2020 by a new protection framework for low pensions. Greece's lenders wanted the benefit scrapped.
VAT
Greece to extend the scope of its 23 percent value-added tax rate, but keep reduced rates of 13 percent for electricity, basic foods, hotels and restaurants and 6 percent for medical supplies and books. Officials said lenders had asked for only two rates: one of 23 percent that would take in electricity and restaurants, and one of 11 percent, to include medicines.
VAT discounts for certain islands to be scrapped, something that Tsipras' coalition partners, the Independent Greeks, have said they will not accept.
INCOME TAX HIKE FOR HIGH EARNERS
Solidarity tax for higher earners to be increased. Officials said this would apply to incomes above 50,000 euros, while the tax would be reduced for incomes below 30,000 euros.
CORPORATE AND LUXURY TAX HIKES
An increase in corporate income tax in 2016 to 29 percent from 26 percent.
A one-off levy in 2015 of 12 percent on businesses that post a profit of over 500,000 euros.
Increases in luxury tax on pools, planes, big cars and private boats over 10 metres (33 feet).
A tax on gambling slot machines (VLTs).
PRIVATISATIONS
Privatisation targets, excluding bank shares, are: 1.4 billion euros in 2015, 3.7 billion in 2016, 1.2 billion in 2017.
Privatisations to impose a minimum amount of investment, a commitment by investors to promote the local economy and the retention of a state shareholding.
The transfer of the state's shareholding in the Greek telecoms operator to the privatisation agency will not be part of the lenders' "prior actions", officials said.
Greece will not privatise its power grid operator (ADMIE) nor its dominant power utility PPC, as requested by creditors, officials said.
OTHER MEASURES
Defence spending to be cut by 200 million euros in 2015.
4G and 5G mobile telecommunications licences to be issued.
Public sector wages not to be cut from end-2014 levels.
Special tax deductions for poor residents of islands.
Gas market to be reformed.
PRIMARY BUDGET SURPLUS
Primary budget surplus to be 1 percent in 2015, 2 percent in
2016, 3 percent in 2017 and 3.5 percent in 2018. This is in line
with what Greece's lenders proposed earlier this month, but much
lower than the targets agreed with the previous Greek government
of up to 4.5 percent.
IMPLEMENTATION
Greece is to adopt supplementary 2015 budget effective as of
July 1, as well as a 2016-2019 medium-term fiscal strategy.
The government promises to have the list of reforms,
including VAT and other legislation, approved in parliament "in
a matter of days".
BONDS
Greek officials said Athens had repeated its demand for the
euro zone to lend it money to buy back 27 billion euros of its
bonds from the European Central Bank - effectively rolling over
the debt on more favourable terms.
INVESTMENT
Greece wants the deal to include financing of infrastructure
and new technologies through the European Commission's 315
billion euro investment plan and from EU funds that it was
eligible for in 2007-2013 but did not use.
NUMERICAL TARGETS
Greece plans fiscal measures worth 7.9 billion euros over
2015 and 2016. The measures break down as follows. Figures in
millions of euros, except where indicated:
2015 2016
VAT REFORMS 680 1,360
PENSIONS
Early retirement accruals 60 300
Increase main contributions by 3.9 pct 350 800
Increase pensioner health contributions
(Standard) to 5 pct from 4 pct 135 270
Increase pensioner health contributions
(Supplementary) to 5 pct from 0 0 240
Increase contribution for supplementary funds
to 3.5 pct from 3 pct 120 250
CORPORATE, INCOME TAX
Special 12 pct levy on
companies with profits
above 500,000 euros 945 405
Raise top-rate corporate
tax to 29 pct from 26 pct 0 410
Increase solidarity levy 220 250
OTHER MEASURES
Defence spending 0 200
TV advertising tax 100 100
Luxury goods tax 47 47
Electronic gambling tax 35 225
4G and 5G phone licences 0 350
TOTAL (in millions) 2,692 5,207
(Pct GDP) 1.51 2.87
(Reporting by Renee Maltezou, Angeliki Koutantou and Andreas
Rinke; Writing by Ingrid Melander; Editing by Kevin Liffey)
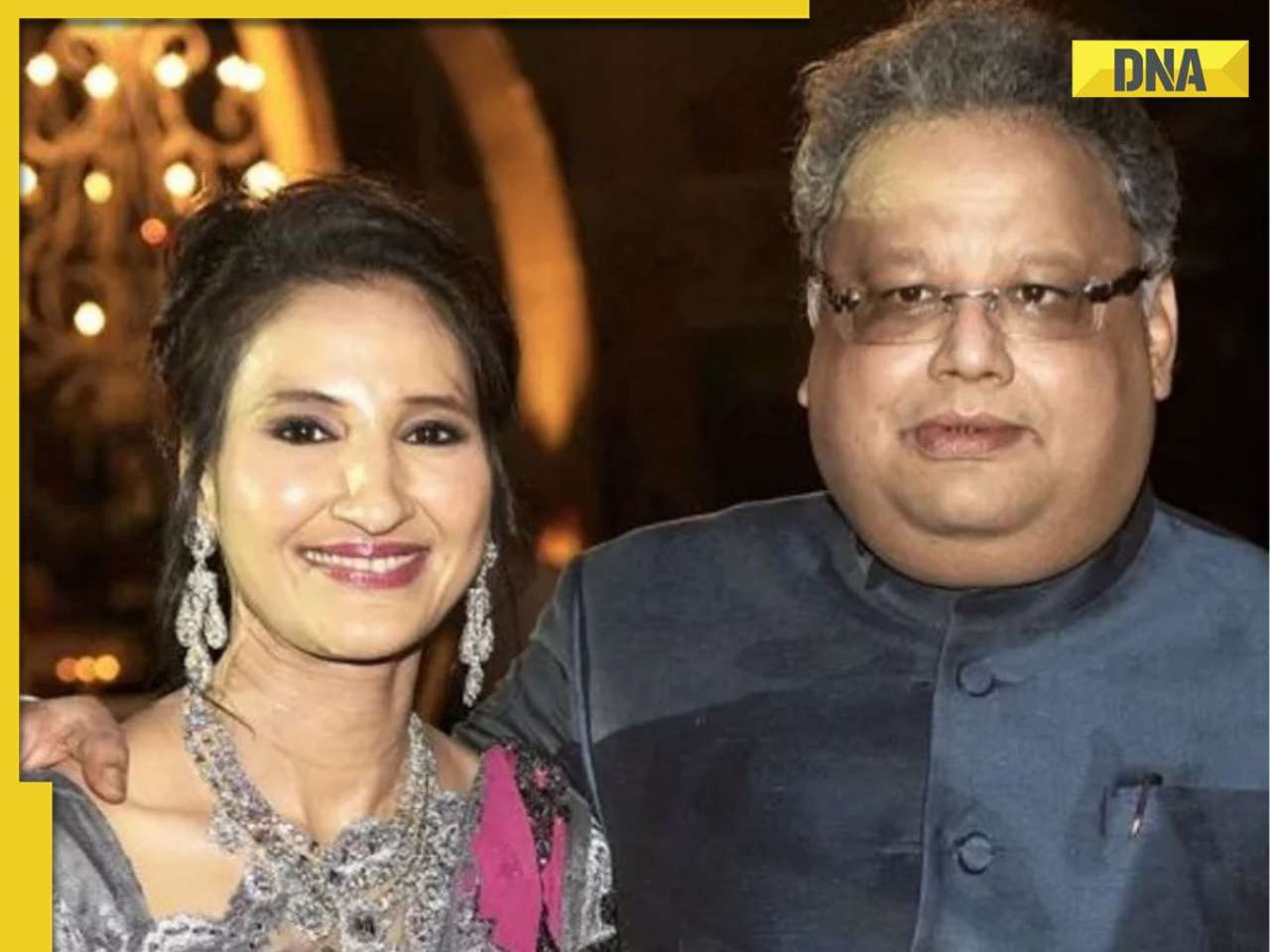
![submenu-img]() Rakesh Jhunjhunwala’s wife sold 734000 shares of this Tata stock, reduced stake in…
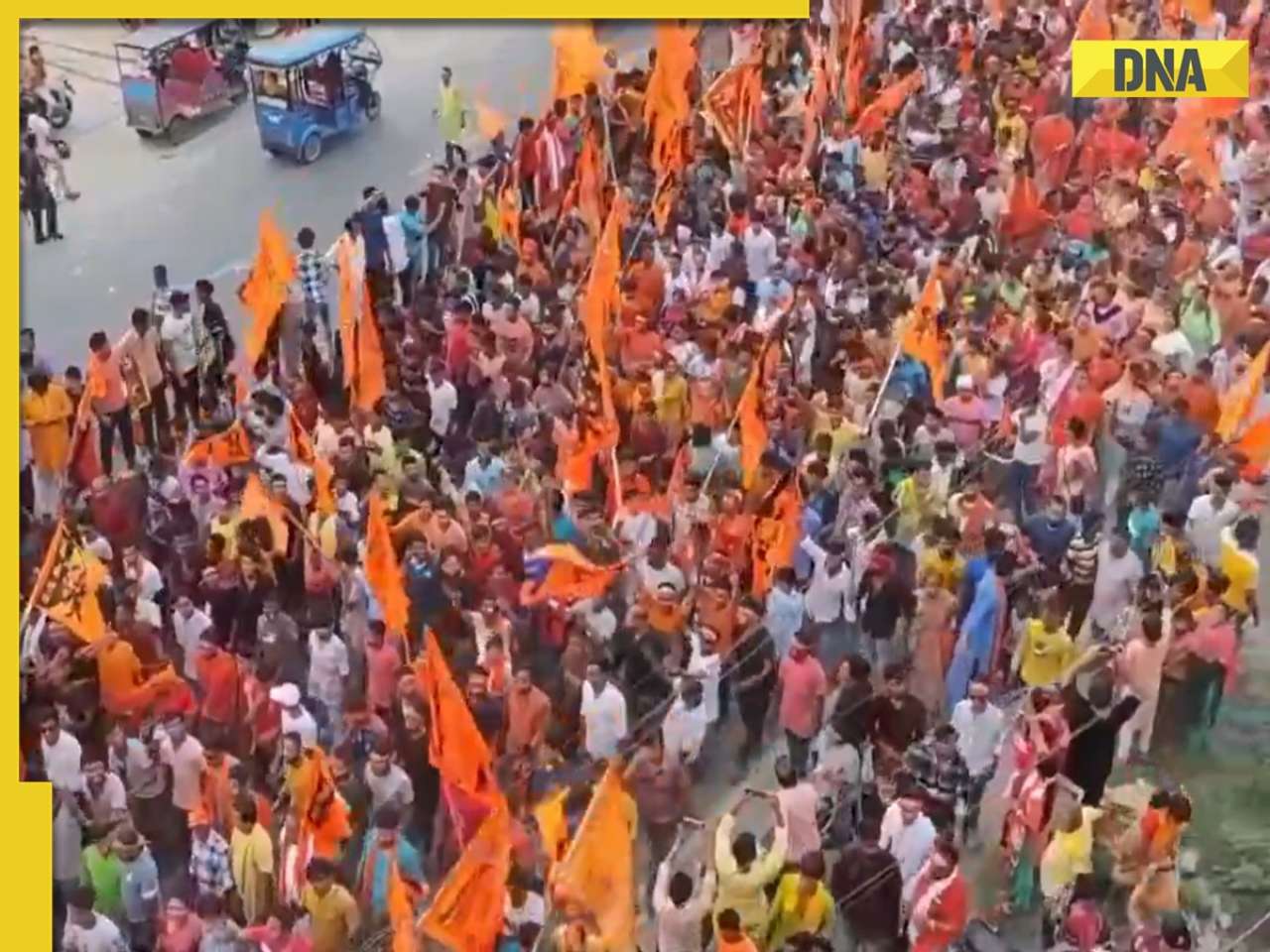
Rakesh Jhunjhunwala’s wife sold 734000 shares of this Tata stock, reduced stake in…![submenu-img]() West Bengal: Ram Navami procession in Murshidabad disrupted by explosion, stone-pelting, BJP reacts
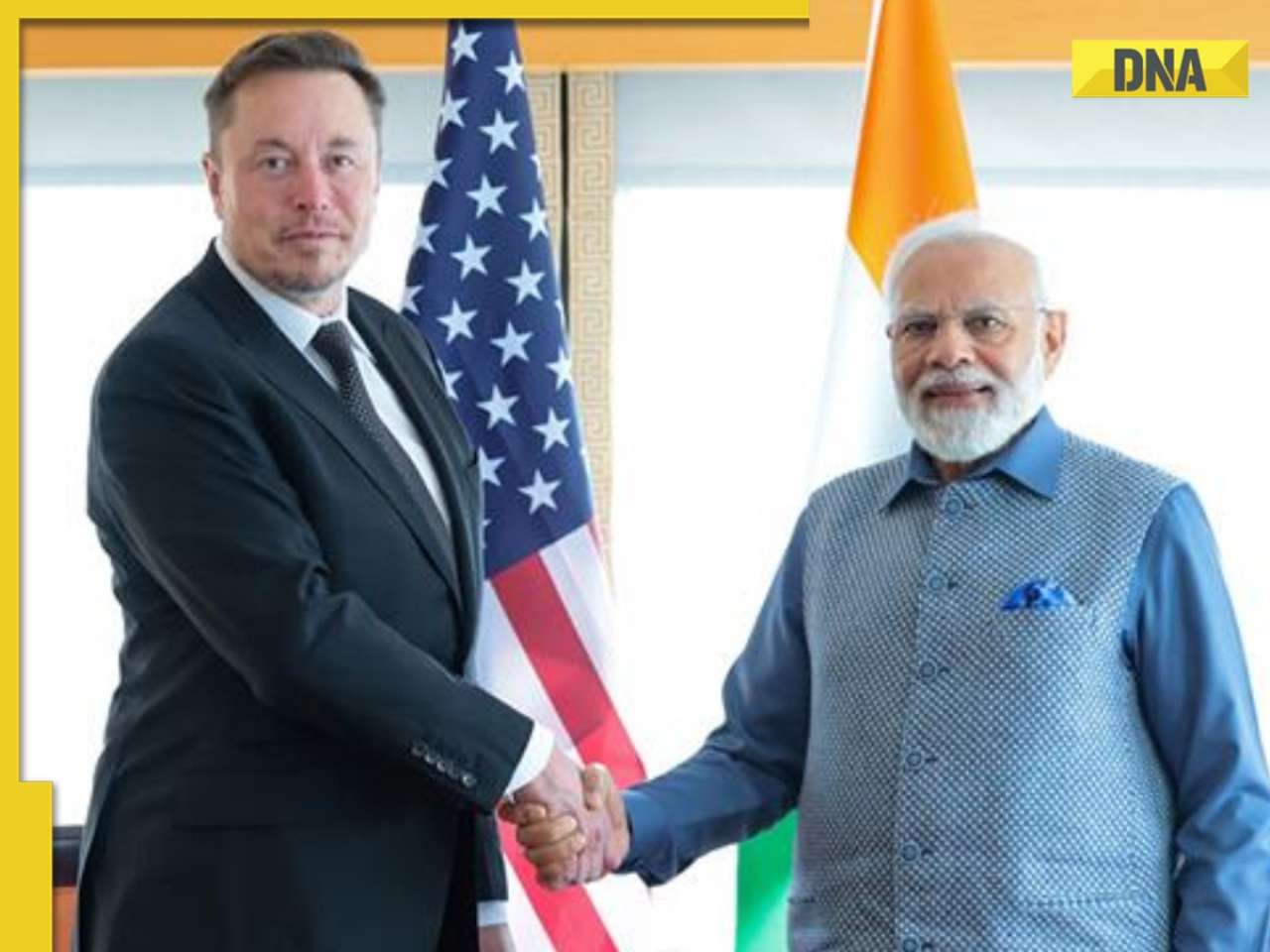
West Bengal: Ram Navami procession in Murshidabad disrupted by explosion, stone-pelting, BJP reacts![submenu-img]() 'We certainly support...': US on Elon Musk's remarks on India's permanent UNSC seat
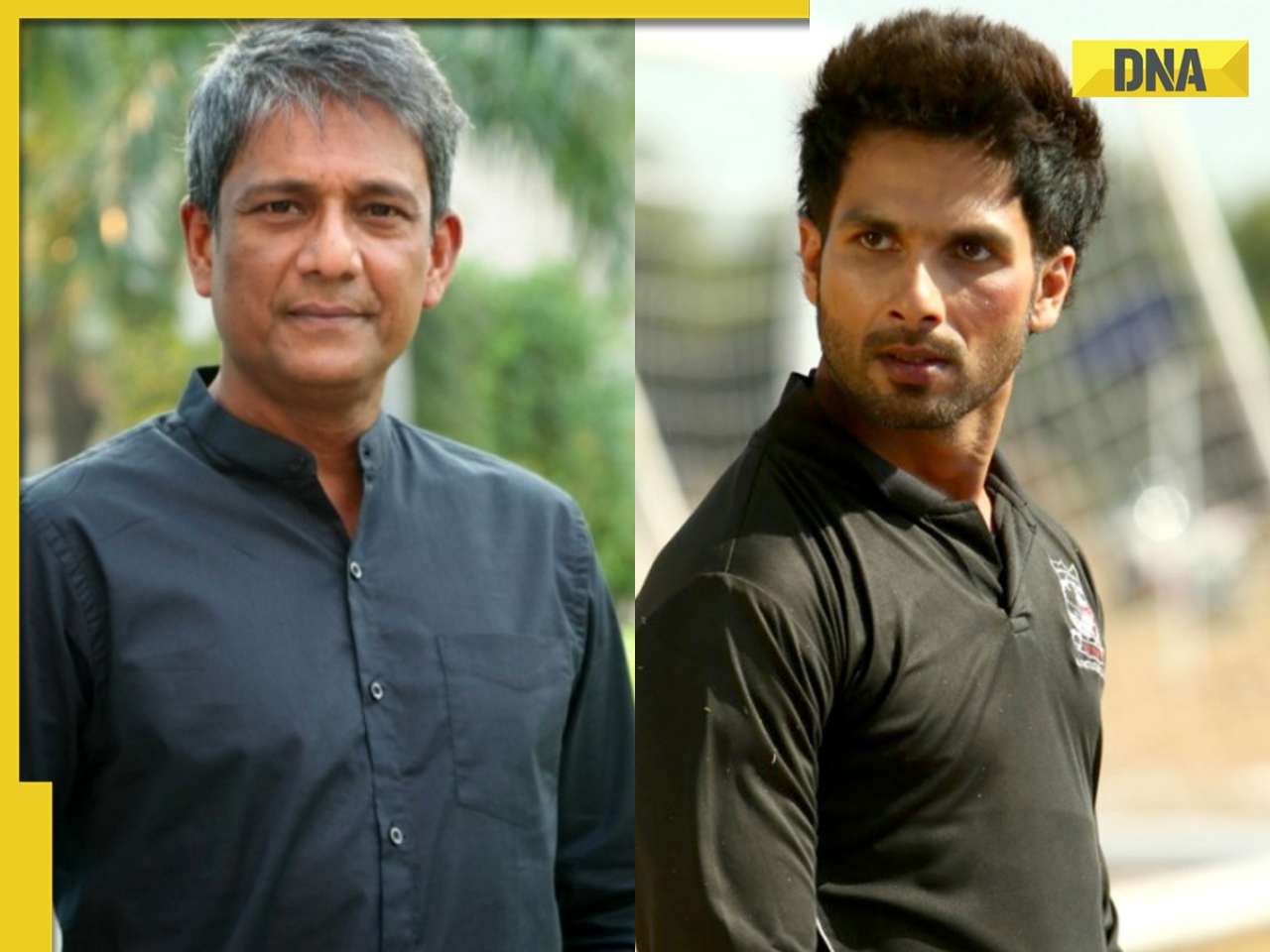
'We certainly support...': US on Elon Musk's remarks on India's permanent UNSC seat![submenu-img]() Adil Hussain regrets doing Sandeep Reddy Vanga’s Kabir Singh, says it makes him feel small: ‘I walked out…’
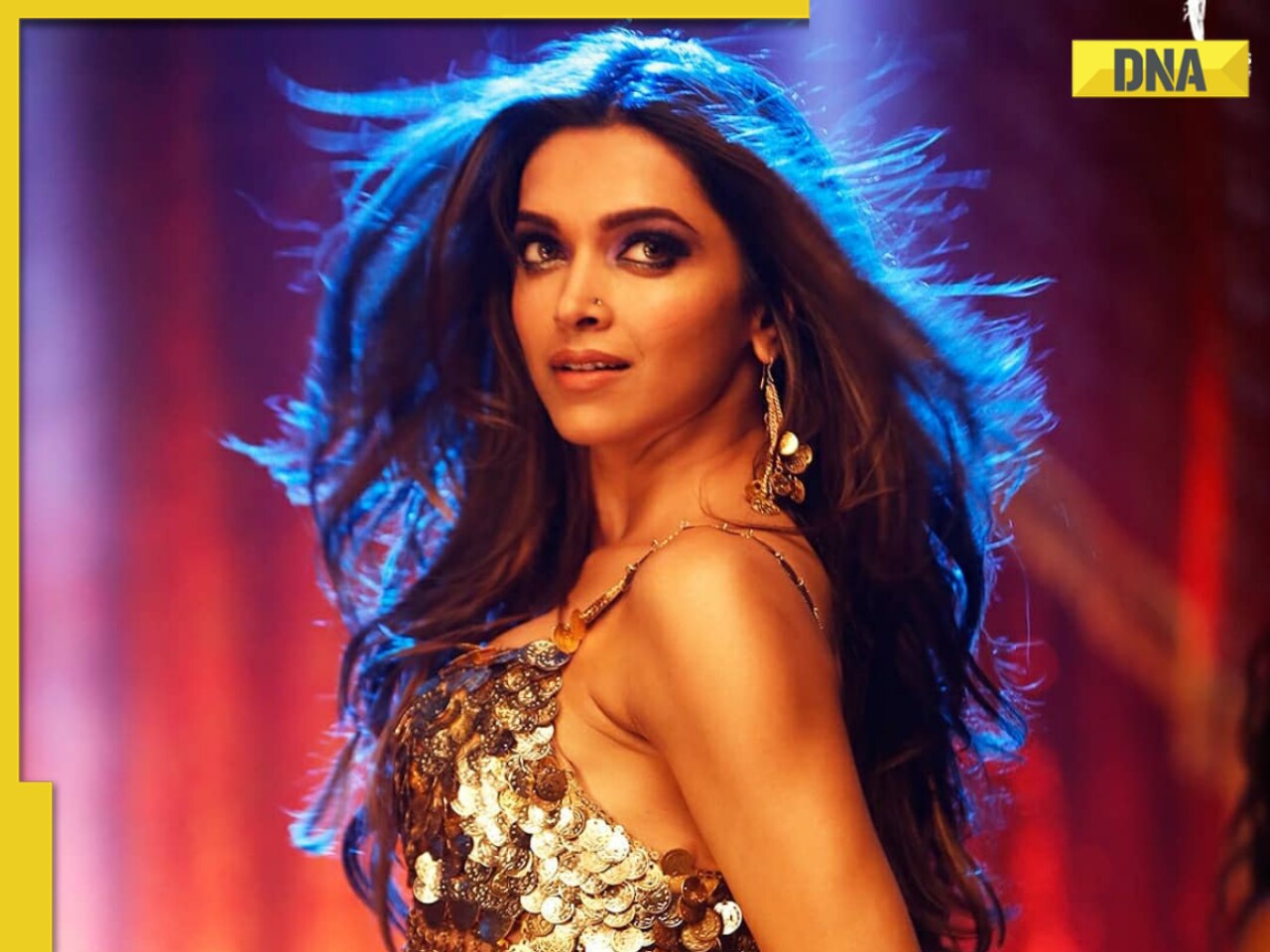
Adil Hussain regrets doing Sandeep Reddy Vanga’s Kabir Singh, says it makes him feel small: ‘I walked out…’![submenu-img]() Deepika Padukone's worst film was delayed for 9 years, panned by critics, called cringefest, still earned Rs 400 crore
Deepika Padukone's worst film was delayed for 9 years, panned by critics, called cringefest, still earned Rs 400 crore![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'
DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message
DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here
DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar
DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth
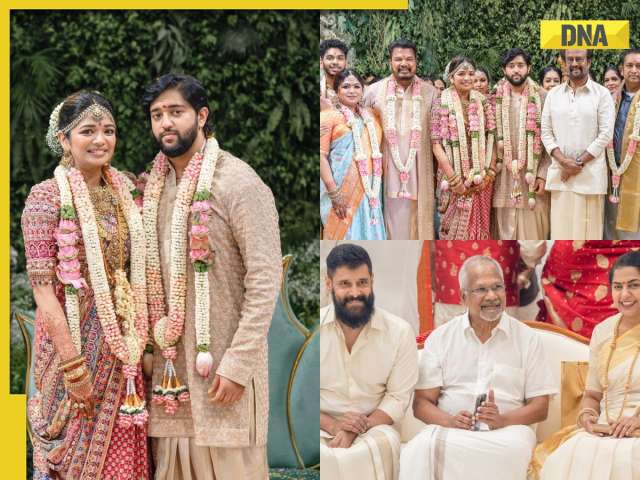
DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth![submenu-img]() In pics: Rajinikanth, Kamal Haasan, Mani Ratnam, Suriya attend S Shankar's daughter Aishwarya's star-studded wedding
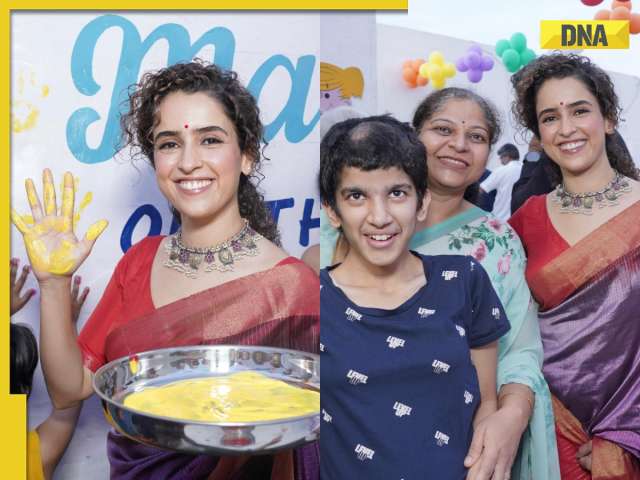
In pics: Rajinikanth, Kamal Haasan, Mani Ratnam, Suriya attend S Shankar's daughter Aishwarya's star-studded wedding![submenu-img]() In pics: Sanya Malhotra attends opening of school for neurodivergent individuals to mark World Autism Month
In pics: Sanya Malhotra attends opening of school for neurodivergent individuals to mark World Autism Month![submenu-img]() Remember Jibraan Khan? Shah Rukh's son in Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham, who worked in Brahmastra; here’s how he looks now
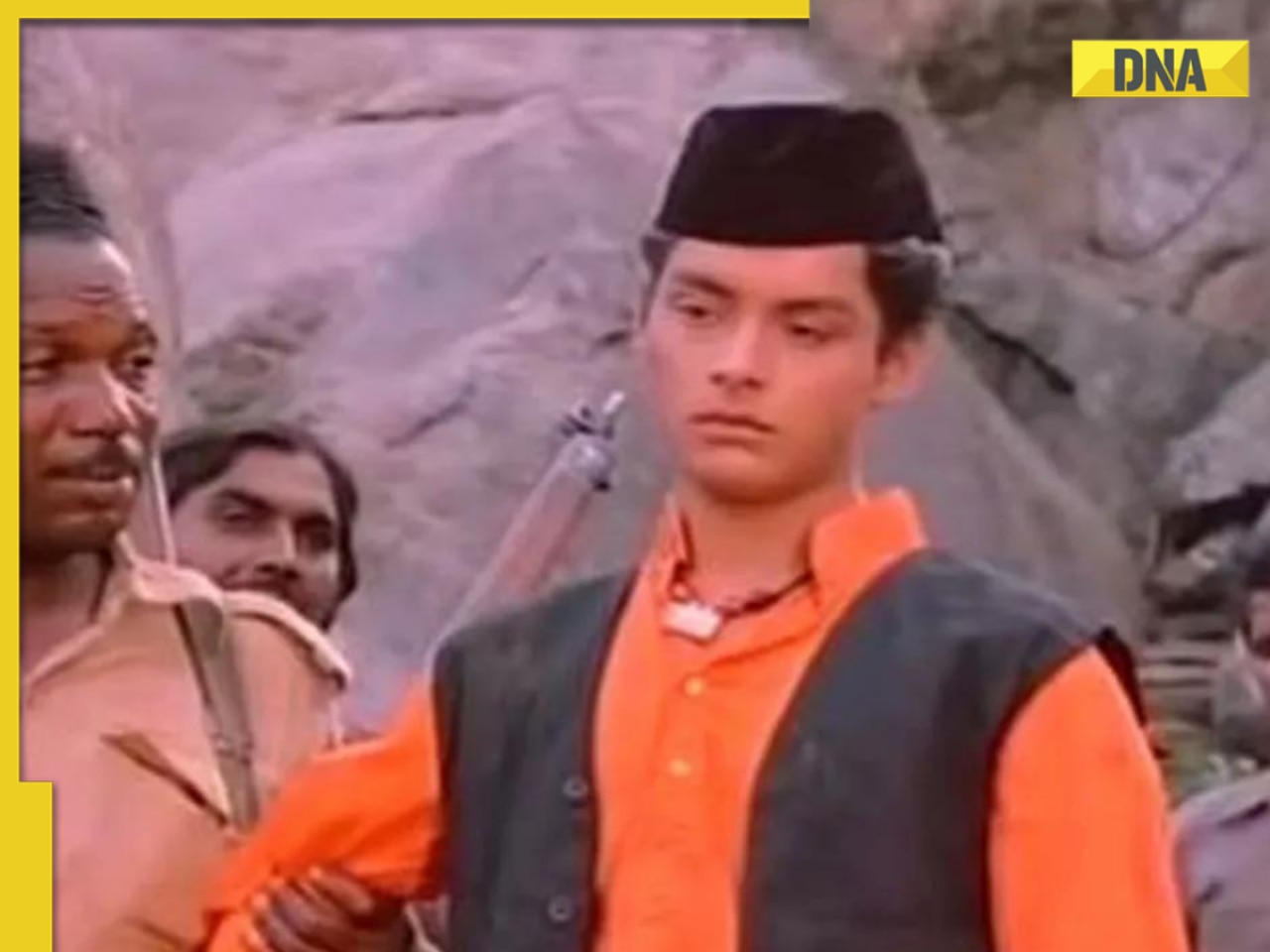
Remember Jibraan Khan? Shah Rukh's son in Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham, who worked in Brahmastra; here’s how he looks now![submenu-img]() From Bade Miyan Chote Miyan to Aavesham: Indian movies to watch in theatres this weekend
From Bade Miyan Chote Miyan to Aavesham: Indian movies to watch in theatres this weekend ![submenu-img]() Streaming This Week: Amar Singh Chamkila, Premalu, Fallout, latest OTT releases to binge-watch
Streaming This Week: Amar Singh Chamkila, Premalu, Fallout, latest OTT releases to binge-watch![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is cloud seeding which is blamed for wreaking havoc in Dubai?
DNA Explainer: What is cloud seeding which is blamed for wreaking havoc in Dubai?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?
DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: How Iranian projectiles failed to breach iron-clad Israeli air defence
DNA Explainer: How Iranian projectiles failed to breach iron-clad Israeli air defence![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is India's stand amid Iran-Israel conflict?
DNA Explainer: What is India's stand amid Iran-Israel conflict?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: Why Iran attacked Israel with hundreds of drones, missiles
DNA Explainer: Why Iran attacked Israel with hundreds of drones, missiles![submenu-img]() Adil Hussain regrets doing Sandeep Reddy Vanga’s Kabir Singh, says it makes him feel small: ‘I walked out…’
Adil Hussain regrets doing Sandeep Reddy Vanga’s Kabir Singh, says it makes him feel small: ‘I walked out…’![submenu-img]() Deepika Padukone's worst film was delayed for 9 years, panned by critics, called cringefest, still earned Rs 400 crore
Deepika Padukone's worst film was delayed for 9 years, panned by critics, called cringefest, still earned Rs 400 crore![submenu-img]() India's first female villain was called Pak spy; married at 14, became mother at 16, left family to run away with star
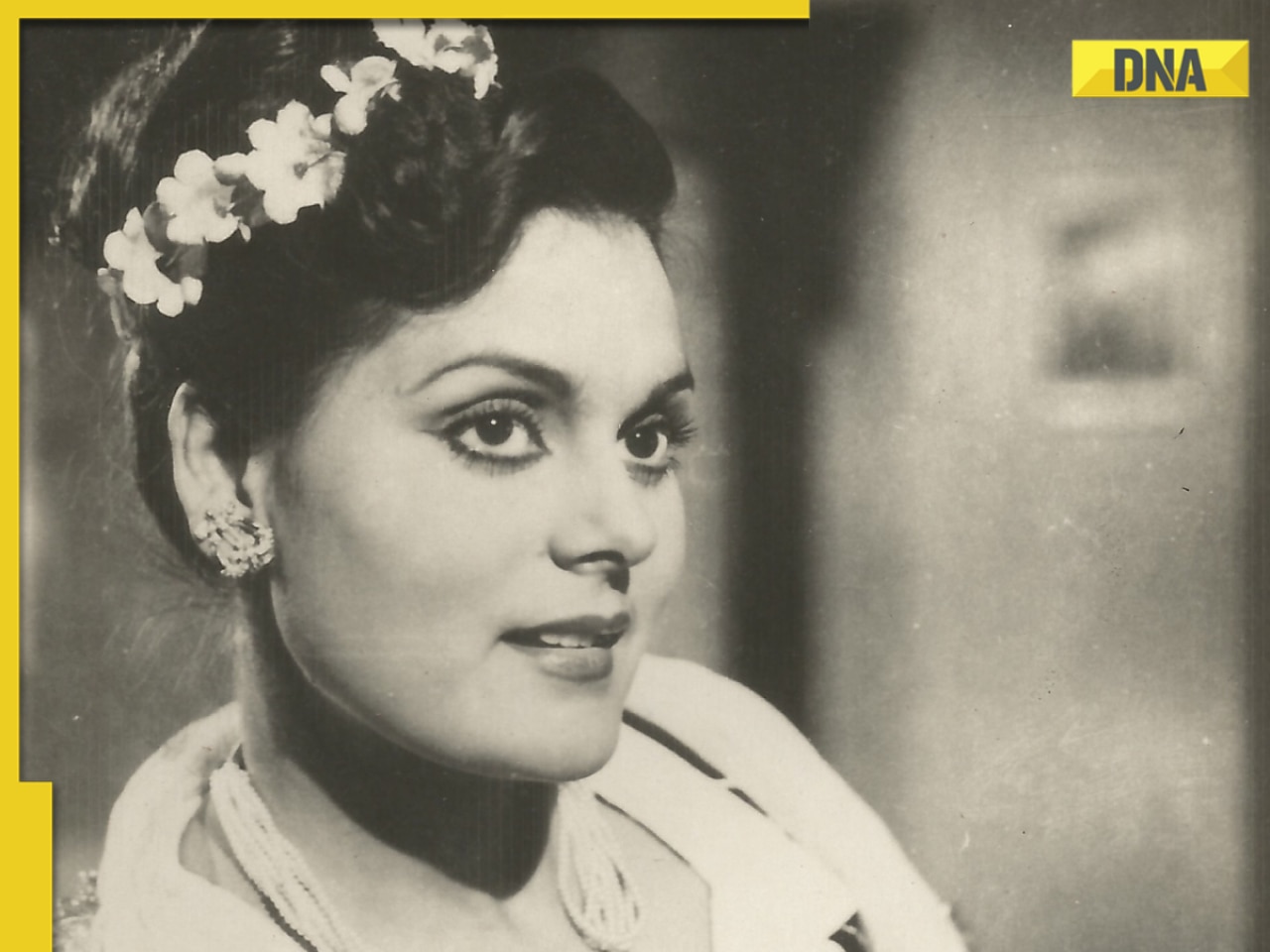
India's first female villain was called Pak spy; married at 14, became mother at 16, left family to run away with star![submenu-img]() Dibakar Banerjee says people didn’t care when Sushant Singh Rajput died, only wanted ‘spicy gossip’: ‘Everyone was…'
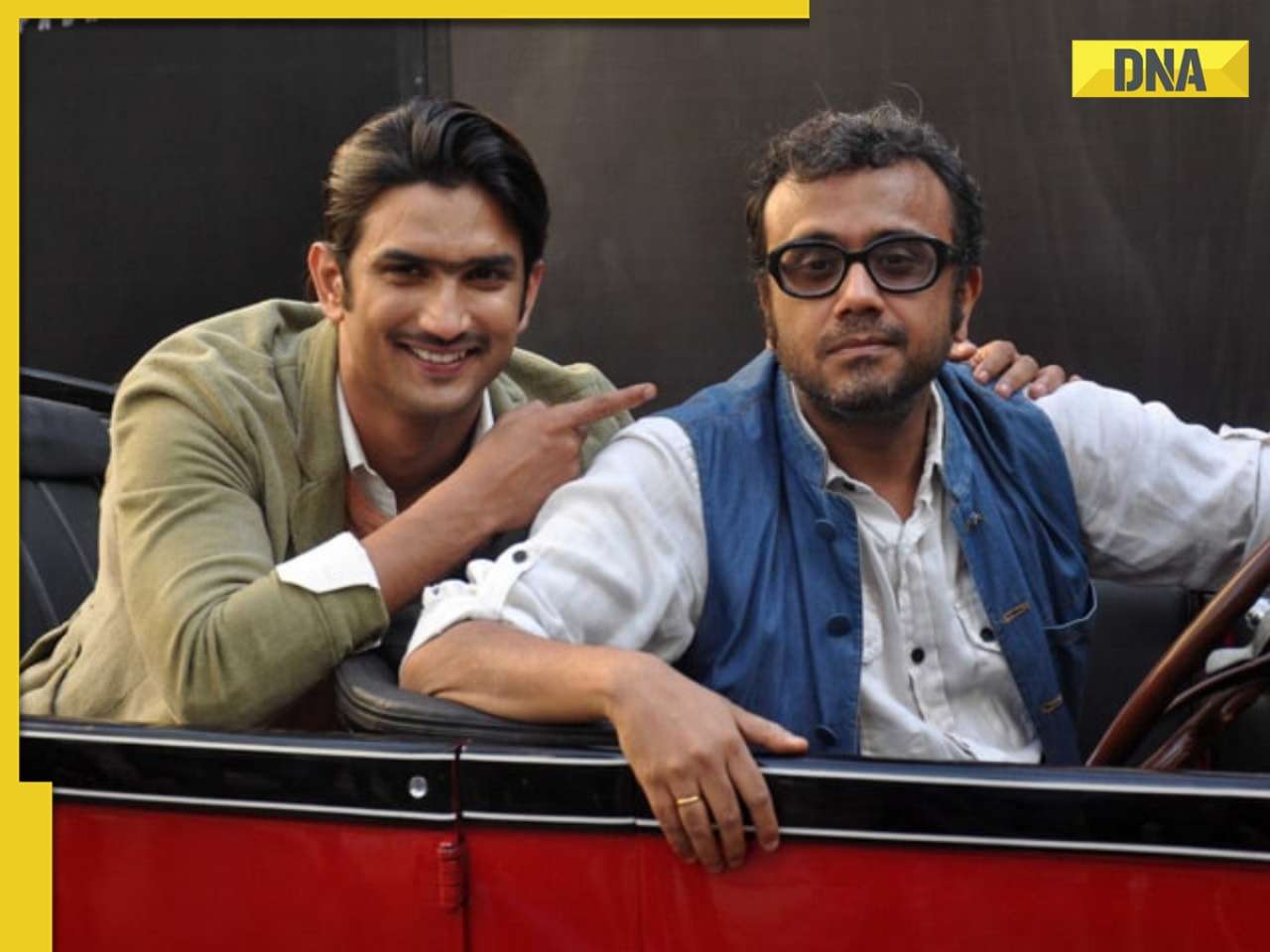
Dibakar Banerjee says people didn’t care when Sushant Singh Rajput died, only wanted ‘spicy gossip’: ‘Everyone was…'![submenu-img]() Most watched Indian film sold 25 crore tickets, was still called flop; not Baahubali, Mughal-e-Azam, Dangal, Jawan, RRR
Most watched Indian film sold 25 crore tickets, was still called flop; not Baahubali, Mughal-e-Azam, Dangal, Jawan, RRR![submenu-img]() IPL 2024: DC thrash GT by 6 wickets as bowlers dominate in Ahmedabad
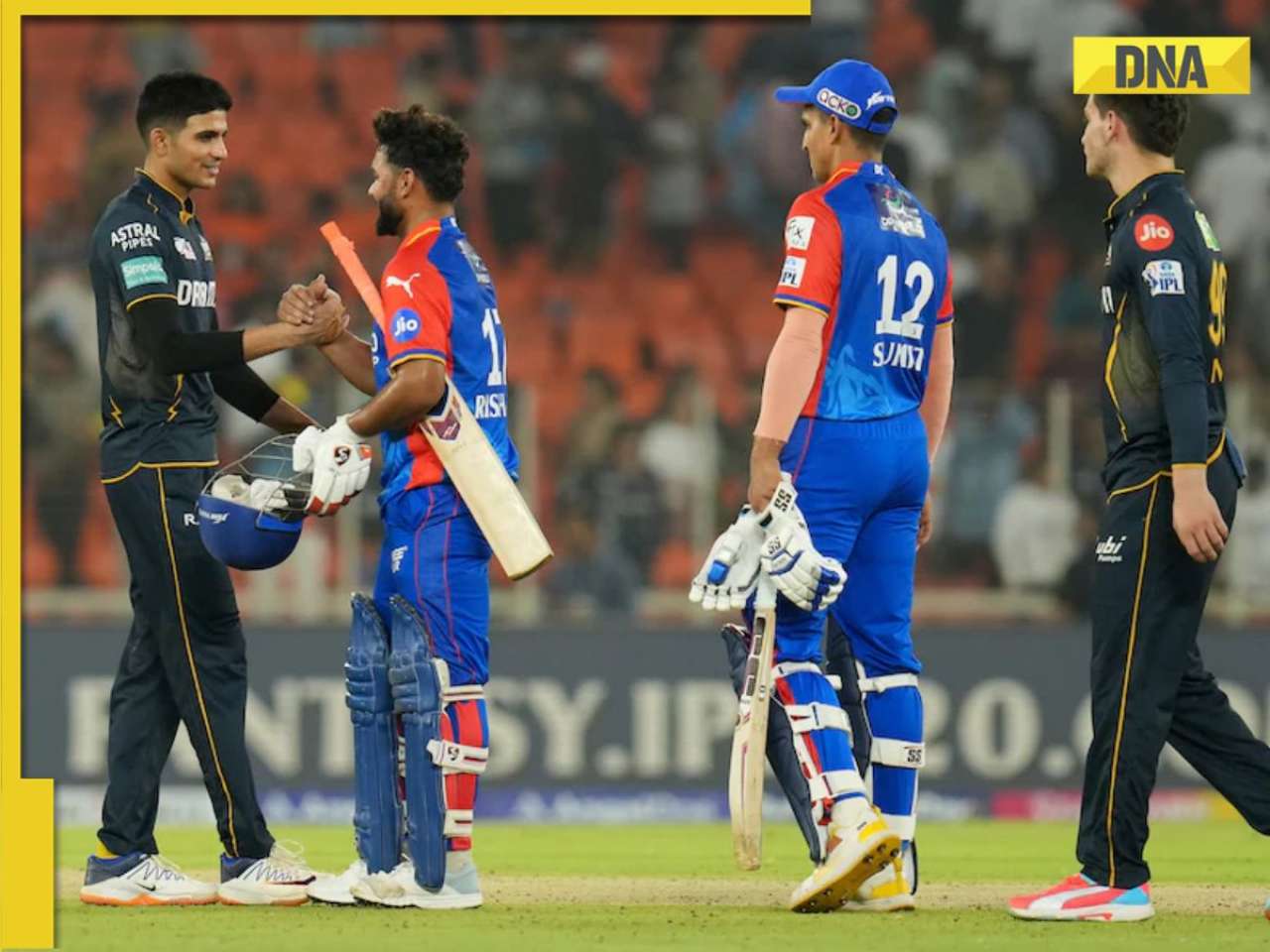
IPL 2024: DC thrash GT by 6 wickets as bowlers dominate in Ahmedabad![submenu-img]() MI vs PBKS, IPL 2024: Predicted playing XI, live streaming details, weather and pitch report
MI vs PBKS, IPL 2024: Predicted playing XI, live streaming details, weather and pitch report![submenu-img]() MI vs PBKS IPL 2024 Dream11 prediction: Fantasy cricket tips for Mumbai Indians vs Punjab Kings
MI vs PBKS IPL 2024 Dream11 prediction: Fantasy cricket tips for Mumbai Indians vs Punjab Kings ![submenu-img]() IPL 2024: Big boost for LSG as star pacer rejoins team, check details
IPL 2024: Big boost for LSG as star pacer rejoins team, check details![submenu-img]() IPL 2024: Jos Buttler's century power RR to 2-wicket win over KKR
IPL 2024: Jos Buttler's century power RR to 2-wicket win over KKR![submenu-img]() This Swiss Alps wedding outshine Mukesh Ambani's son Anant Ambani's Jamnagar pre-wedding gala
This Swiss Alps wedding outshine Mukesh Ambani's son Anant Ambani's Jamnagar pre-wedding gala![submenu-img]() Watch viral video: Deserts around Saudi Arabia's Mecca and Medina are turning green due to…
Watch viral video: Deserts around Saudi Arabia's Mecca and Medina are turning green due to…![submenu-img]() Shocking details about 'Death Valley', one of the world's hottest places
Shocking details about 'Death Valley', one of the world's hottest places![submenu-img]() Aditya Srivastava's first reaction after UPSC CSE 2023 result goes viral, watch video here
Aditya Srivastava's first reaction after UPSC CSE 2023 result goes viral, watch video here![submenu-img]() Watch viral video: Isha Ambani, Shloka Mehta, Anant Ambani spotted at Janhvi Kapoor's home
Watch viral video: Isha Ambani, Shloka Mehta, Anant Ambani spotted at Janhvi Kapoor's home






































)




)
)
)
)
)
)