Despite volatility and the slowdown after 2007-2008 Odisha was able to achieve revenue and fiscal surplus and reduced the debt burden substantially in 2012-13 in the post FRBM period, says a government report.
The National Institute of Public Finance and Policy (NIPFP) report was presented in the state Assembly on Monday by Finance Minister Pradip Kumar Amat.
"Odisha government consistently maintained strong fiscal position during the post FRBM (Fiscal Responsibility & Budget Management) period," the report said.
While budget projections for the year with regard to major fiscal outcomes were within FRBM Act stipulation, the state government managed to achieve improved out turns. In 2012-13, the revenue surplus was substantial at 2.23% relative to GSDP and the state enjoyed a fiscal surplus situation, it said.
The outstanding debt burden was only 14.87% of GSDP, which was well below the 30.2% level recommended as prudent by the 13th Finance Commission. Compared to the fiscal targets specified for the year in the amended FRBM Act, 2011, a zero revenue deficit, fiscal deficit limit of 3% of GSDP, and debt burden of 30.2% to the GSDP were acheived by the state.
"These achievements were commendable," the report said.
As against a target of interest payment as percentage of revenue receipts at 15%, the achievement has been only 6.39%, the report stated.
The compression of both revenue and capital expenditure as compared to the budget estimates was the major instrument to achieve large revenue surplus and elimination of fiscal deficit in the fiscal year 2012-13.
However, actual revenue realisation exceeded the target marginally, the report said. It was the higher realisation of non-tax revenue that helped in meeting the revenue target as own tax receipts and central grants fell below the budget projections.
With rising revenue surplus and slow growing capital expenditure, the government reduced its dependence on market borrowing and even discharged some high cost loans to bring down its overall debt stock.
The state government accumulated a large cash balance 2012-13, which was invested in Government of India treasury bills with RBI, it said. However, compliance to the fiscal management principles enunciated in the act should not be neglected.
One of the important principles has been to formulate a realistic budget by giving due regard to the general economic outlook to minimise the deviation from the budget projections during the year.
The decline in own tax revenue as compared to the budget estimates in 2012-13 despite a higher GSDP growth over the last year does not satisfy the observance of this principle, it said. "The examination of the budget estimaetes and actual expenditure during 2012-13 shows that under many heads the budgetary provisions were not fully utilised," the report said adding actual expenditure for some of the important sectors like education, water supply and sanitation, and irrigation and flood control were less than that of the budget estimates.
Although the state government managed to generate a large revenue surplus - substantially more than the budget estimates, the capital expenditure as percentage of GSDP has remained subdued in recent yars, it said.
The NIPFP suggested that the comfortable cash balance position and emergence of substantial surplus in revenue account should enable the government to restructure the expenditure pattern focusing on priority sectors and infastructure building.
The assessment of the spending pattern revealed that under-spending in several high-priority sectors was more due to capacity problems rather than the objective of compressing the overall expenditure.
The improvement in fiscal position of the government and emergence of comfortable resource position should lead to effective policy actions for removing the impediments to better utilisation of budgetd provisions and larger allocations to priority sectors, it said.
Strengthening capacity to improve project conceptualisation and implementation in infrastructure sector should be the key objective of the government policies.
The government also should pay attention to facilitate land acquisition, improve coordination among departments at policy and implementation level and speed up environment clearances from central agencies for better implemenation of projets and utilisation of the aproved budget, the report added.
![submenu-img]() Anushka Sharma, Virat Kohli officially reveal newborn son Akaay's face but only to...
Anushka Sharma, Virat Kohli officially reveal newborn son Akaay's face but only to...![submenu-img]() Elon Musk's Tesla to fire more than 14000 employees, preparing company for...
Elon Musk's Tesla to fire more than 14000 employees, preparing company for...![submenu-img]() Meet man, who cracked UPSC exam, then quit IAS officer's post to become monk due to...
Meet man, who cracked UPSC exam, then quit IAS officer's post to become monk due to...![submenu-img]() How Imtiaz Ali failed Amar Singh Chamkila, and why a good film can also be a bad biopic | Opinion
How Imtiaz Ali failed Amar Singh Chamkila, and why a good film can also be a bad biopic | Opinion![submenu-img]() Ola S1 X gets massive price cut, electric scooter price now starts at just Rs…
Ola S1 X gets massive price cut, electric scooter price now starts at just Rs…![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'
DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message
DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here
DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar
DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth
DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth![submenu-img]() In pics: Rajinikanth, Kamal Haasan, Mani Ratnam, Suriya attend S Shankar's daughter Aishwarya's star-studded wedding
In pics: Rajinikanth, Kamal Haasan, Mani Ratnam, Suriya attend S Shankar's daughter Aishwarya's star-studded wedding![submenu-img]() In pics: Sanya Malhotra attends opening of school for neurodivergent individuals to mark World Autism Month
In pics: Sanya Malhotra attends opening of school for neurodivergent individuals to mark World Autism Month![submenu-img]() Remember Jibraan Khan? Shah Rukh's son in Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham, who worked in Brahmastra; here’s how he looks now
Remember Jibraan Khan? Shah Rukh's son in Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham, who worked in Brahmastra; here’s how he looks now![submenu-img]() From Bade Miyan Chote Miyan to Aavesham: Indian movies to watch in theatres this weekend
From Bade Miyan Chote Miyan to Aavesham: Indian movies to watch in theatres this weekend ![submenu-img]() Streaming This Week: Amar Singh Chamkila, Premalu, Fallout, latest OTT releases to binge-watch
Streaming This Week: Amar Singh Chamkila, Premalu, Fallout, latest OTT releases to binge-watch![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?
DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: How Iranian projectiles failed to breach iron-clad Israeli air defence
DNA Explainer: How Iranian projectiles failed to breach iron-clad Israeli air defence![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is India's stand amid Iran-Israel conflict?
DNA Explainer: What is India's stand amid Iran-Israel conflict?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: Why Iran attacked Israel with hundreds of drones, missiles
DNA Explainer: Why Iran attacked Israel with hundreds of drones, missiles![submenu-img]() What is Katchatheevu island row between India and Sri Lanka? Why it has resurfaced before Lok Sabha Elections 2024?
What is Katchatheevu island row between India and Sri Lanka? Why it has resurfaced before Lok Sabha Elections 2024?![submenu-img]() Anushka Sharma, Virat Kohli officially reveal newborn son Akaay's face but only to...
Anushka Sharma, Virat Kohli officially reveal newborn son Akaay's face but only to...![submenu-img]() How Imtiaz Ali failed Amar Singh Chamkila, and why a good film can also be a bad biopic | Opinion
How Imtiaz Ali failed Amar Singh Chamkila, and why a good film can also be a bad biopic | Opinion![submenu-img]() Aamir Khan files FIR after video of him 'promoting particular party' circulates ahead of Lok Sabha elections: 'We are..'
Aamir Khan files FIR after video of him 'promoting particular party' circulates ahead of Lok Sabha elections: 'We are..'![submenu-img]() Henry Cavill and girlfriend Natalie Viscuso expecting their first child together, actor says 'I'm very excited'
Henry Cavill and girlfriend Natalie Viscuso expecting their first child together, actor says 'I'm very excited'![submenu-img]() This actress was thrown out of films, insulted for her looks, now owns private jet, sea-facing bungalow worth Rs...
This actress was thrown out of films, insulted for her looks, now owns private jet, sea-facing bungalow worth Rs...![submenu-img]() IPL 2024: Travis Head, Heinrich Klaasen power SRH to 25 run win over RCB
IPL 2024: Travis Head, Heinrich Klaasen power SRH to 25 run win over RCB![submenu-img]() KKR vs RR, IPL 2024: Predicted playing XI, live streaming details, weather and pitch report
KKR vs RR, IPL 2024: Predicted playing XI, live streaming details, weather and pitch report![submenu-img]() KKR vs RR IPL 2024 Dream11 prediction: Fantasy cricket tips for Kolkata Knight Riders vs Rajasthan Royals
KKR vs RR IPL 2024 Dream11 prediction: Fantasy cricket tips for Kolkata Knight Riders vs Rajasthan Royals![submenu-img]() RCB vs SRH, IPL 2024: Predicted playing XI, live streaming details, weather and pitch report
RCB vs SRH, IPL 2024: Predicted playing XI, live streaming details, weather and pitch report![submenu-img]() IPL 2024: Rohit Sharma's century goes in vain as CSK beat MI by 20 runs
IPL 2024: Rohit Sharma's century goes in vain as CSK beat MI by 20 runs![submenu-img]() Watch viral video: Isha Ambani, Shloka Mehta, Anant Ambani spotted at Janhvi Kapoor's home
Watch viral video: Isha Ambani, Shloka Mehta, Anant Ambani spotted at Janhvi Kapoor's home![submenu-img]() This diety holds special significance for Mukesh Ambani, Nita Ambani, Isha Ambani, Akash, Anant , it is located in...
This diety holds special significance for Mukesh Ambani, Nita Ambani, Isha Ambani, Akash, Anant , it is located in...![submenu-img]() Swiggy delivery partner steals Nike shoes kept outside flat, netizens react, watch viral video
Swiggy delivery partner steals Nike shoes kept outside flat, netizens react, watch viral video![submenu-img]() iPhone maker Apple warns users in India, other countries of this threat, know alert here
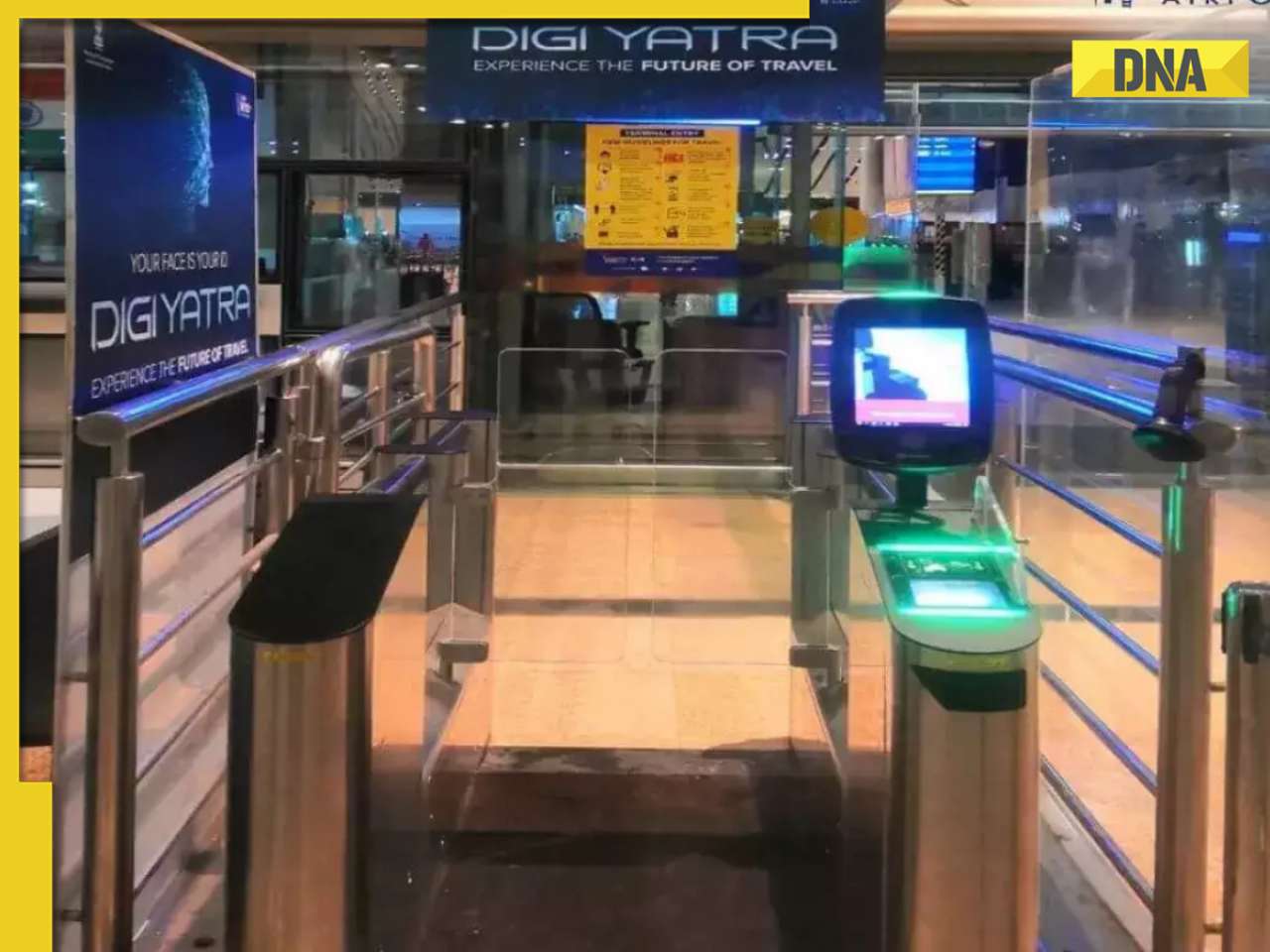
iPhone maker Apple warns users in India, other countries of this threat, know alert here![submenu-img]() Old Digi Yatra app will not work at airports, know how to download new app
Old Digi Yatra app will not work at airports, know how to download new app






































)




)
)
)
)
)
)