Significant changes were observed in meditators and vacations after one week at the resort
Researchers in the USA have studied the effects that a week's vacation and a week's meditation can have on our bodies and minds.
According to this new study, published in the journal Translational Psychiatry (Nature), meditation could boost metabolism long-term whereas straightforward vacations may favour short-term improvements in well-being.
As well as relaxing the body and mind, meditation could have a biological impact on stress response and immune function long-term. Researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, the University of California and Harvard Medical School followed 94 healthy women aged from 30 to 60 years old, who all spent a week on vacation at the same resort. Half of the group followed a meditation program including mantra meditation, yoga and self-reflection exercises. The scientists also studied a group of 30 meditators who were already signed up for the week-long retreat.
Blood samples were collected from participants, as well as surveys, before and after their stay. The samples were tested for biomarkers associated with stress, cell health and ageing. Surveys were also collected one month and 10 months after the experience. The scientists studied changes in 20,000 genes in all three groups to establish which genes were subject to changes before and after the week-long break.
Significant changes were observed in novice meditators, experienced meditators and vacations after one week at the resort. The scientists put this down to the "vacation effect," brought about in relaxing environments. The most notable changes were found in genes relating to stress response and immune function.
The benefits strongly increased for experienced meditators during the vacation period. When asked about their well-being one month after the experience, all participants reported feeling better. However, the novice meditators experienced fewer symptoms of depression and lower stress levels long-term than the vacationers who didn't meditate. The psychological effects also appeared to be lasting.
The scientists suggest that meditation could help improve metabolism by protecting cells long-term, whereas classic vacations may favor more short-term improvements in mental well-being. "Meditation is one of the ways to engage in restorative activities that may provide relief for our immune systems, easing the day-to-day stress of a body constantly trying to protect itself. The prediction is that this would then lead to healthier aging," said Rudolph Tanzi, professor of neurology at Harvard University.
The study was published in the journal Translational Psychiatry, published by Nature.
![submenu-img]() Rakesh Jhunjhunwala’s wife sold 734000 shares of this Tata stock, reduced stake in…
Rakesh Jhunjhunwala’s wife sold 734000 shares of this Tata stock, reduced stake in…![submenu-img]() West Bengal: Ram Navami procession in Murshidabad disrupted by explosion, stone-pelting, BJP reacts
West Bengal: Ram Navami procession in Murshidabad disrupted by explosion, stone-pelting, BJP reacts![submenu-img]() 'We certainly support...': US on Elon Musk's remarks on India's permanent UNSC seat
'We certainly support...': US on Elon Musk's remarks on India's permanent UNSC seat![submenu-img]() Adil Hussain regrets doing Sandeep Reddy Vanga’s Kabir Singh, says it makes him feel small: ‘I walked out…’
Adil Hussain regrets doing Sandeep Reddy Vanga’s Kabir Singh, says it makes him feel small: ‘I walked out…’![submenu-img]() Deepika Padukone's worst film was delayed for 9 years, panned by critics, called cringefest, still earned Rs 400 crore
Deepika Padukone's worst film was delayed for 9 years, panned by critics, called cringefest, still earned Rs 400 crore![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'
DNA Verified: Is CAA an anti-Muslim law? Centre terms news report as 'misleading'![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message
DNA Verified: Lok Sabha Elections 2024 to be held on April 19? Know truth behind viral message![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here
DNA Verified: Modi govt giving students free laptops under 'One Student One Laptop' scheme? Know truth here![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar
DNA Verified: Shah Rukh Khan denies reports of his role in release of India's naval officers from Qatar![submenu-img]() DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth
DNA Verified: Is govt providing Rs 1.6 lakh benefit to girls under PM Ladli Laxmi Yojana? Know truth![submenu-img]() In pics: Rajinikanth, Kamal Haasan, Mani Ratnam, Suriya attend S Shankar's daughter Aishwarya's star-studded wedding
In pics: Rajinikanth, Kamal Haasan, Mani Ratnam, Suriya attend S Shankar's daughter Aishwarya's star-studded wedding![submenu-img]() In pics: Sanya Malhotra attends opening of school for neurodivergent individuals to mark World Autism Month
In pics: Sanya Malhotra attends opening of school for neurodivergent individuals to mark World Autism Month![submenu-img]() Remember Jibraan Khan? Shah Rukh's son in Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham, who worked in Brahmastra; here’s how he looks now
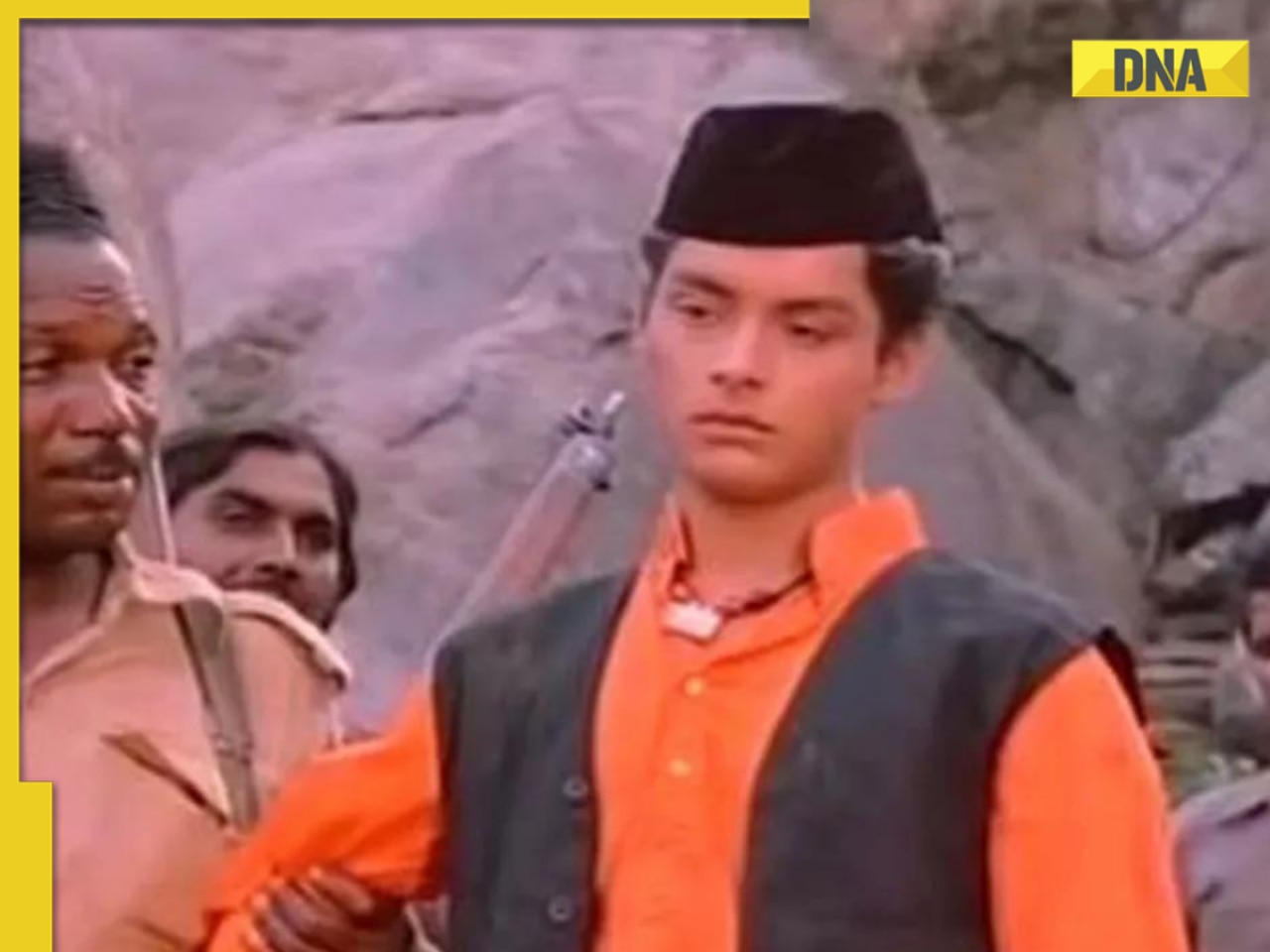
Remember Jibraan Khan? Shah Rukh's son in Kabhi Khushi Kabhie Gham, who worked in Brahmastra; here’s how he looks now![submenu-img]() From Bade Miyan Chote Miyan to Aavesham: Indian movies to watch in theatres this weekend
From Bade Miyan Chote Miyan to Aavesham: Indian movies to watch in theatres this weekend ![submenu-img]() Streaming This Week: Amar Singh Chamkila, Premalu, Fallout, latest OTT releases to binge-watch
Streaming This Week: Amar Singh Chamkila, Premalu, Fallout, latest OTT releases to binge-watch![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is cloud seeding which is blamed for wreaking havoc in Dubai?
DNA Explainer: What is cloud seeding which is blamed for wreaking havoc in Dubai?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?
DNA Explainer: What is Israel's Arrow-3 defence system used to intercept Iran's missile attack?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: How Iranian projectiles failed to breach iron-clad Israeli air defence
DNA Explainer: How Iranian projectiles failed to breach iron-clad Israeli air defence![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: What is India's stand amid Iran-Israel conflict?
DNA Explainer: What is India's stand amid Iran-Israel conflict?![submenu-img]() DNA Explainer: Why Iran attacked Israel with hundreds of drones, missiles
DNA Explainer: Why Iran attacked Israel with hundreds of drones, missiles![submenu-img]() Adil Hussain regrets doing Sandeep Reddy Vanga’s Kabir Singh, says it makes him feel small: ‘I walked out…’
Adil Hussain regrets doing Sandeep Reddy Vanga’s Kabir Singh, says it makes him feel small: ‘I walked out…’![submenu-img]() Deepika Padukone's worst film was delayed for 9 years, panned by critics, called cringefest, still earned Rs 400 crore
Deepika Padukone's worst film was delayed for 9 years, panned by critics, called cringefest, still earned Rs 400 crore![submenu-img]() India's first female villain was called Pak spy; married at 14, became mother at 16, left family to run away with star
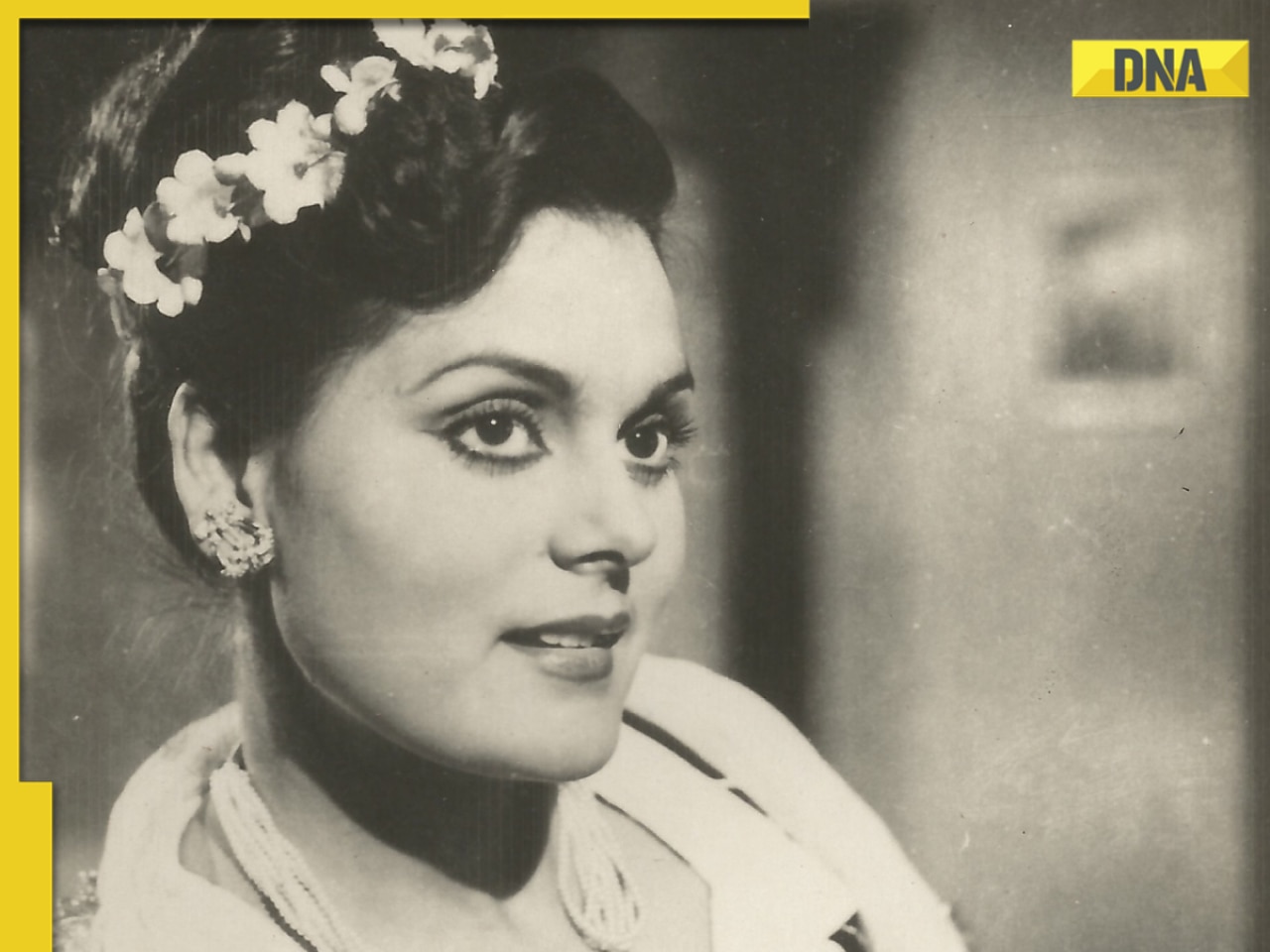
India's first female villain was called Pak spy; married at 14, became mother at 16, left family to run away with star![submenu-img]() Dibakar Banerjee says people didn’t care when Sushant Singh Rajput died, only wanted ‘spicy gossip’: ‘Everyone was…'
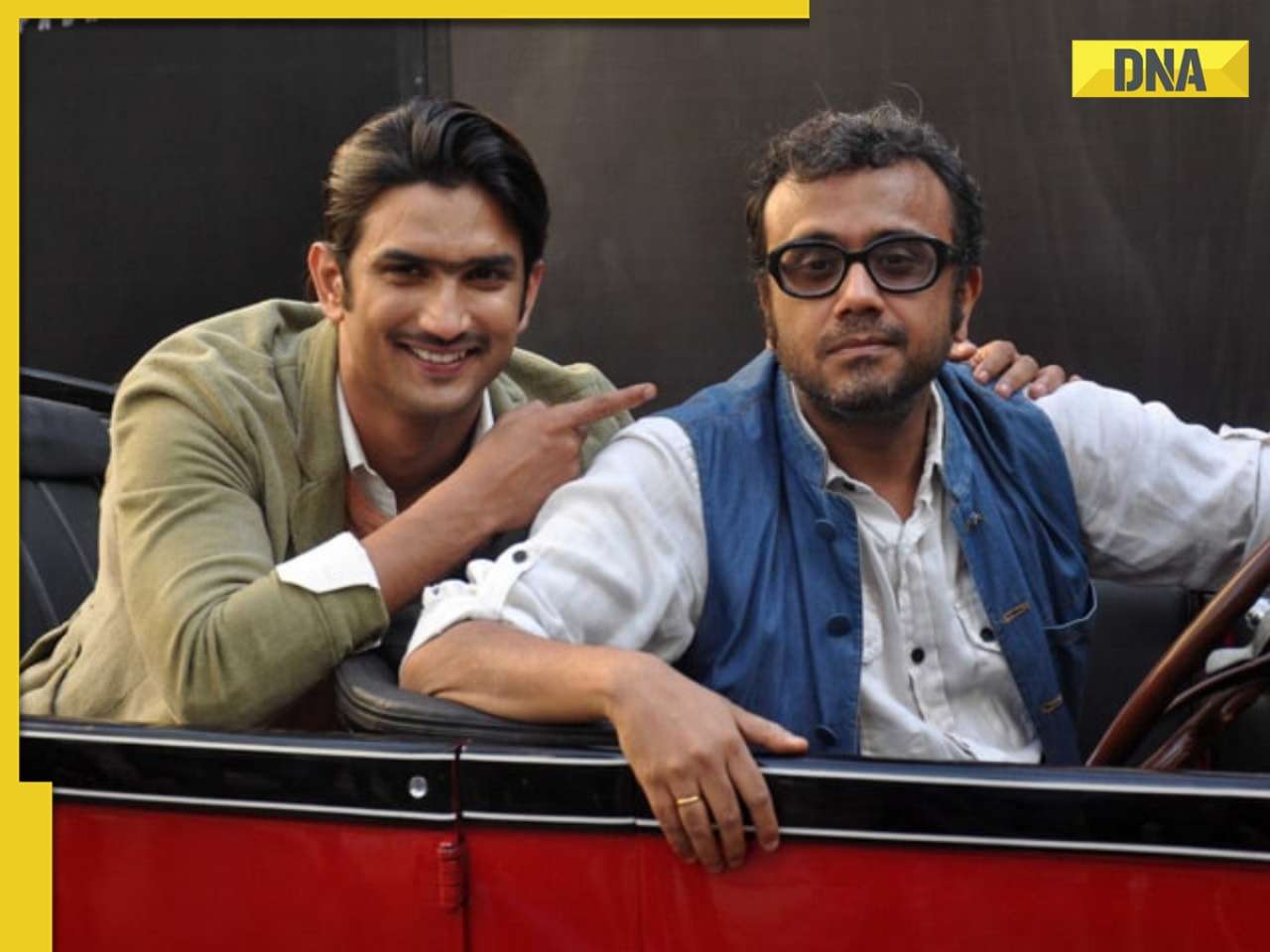
Dibakar Banerjee says people didn’t care when Sushant Singh Rajput died, only wanted ‘spicy gossip’: ‘Everyone was…'![submenu-img]() Most watched Indian film sold 25 crore tickets, was still called flop; not Baahubali, Mughal-e-Azam, Dangal, Jawan, RRR
Most watched Indian film sold 25 crore tickets, was still called flop; not Baahubali, Mughal-e-Azam, Dangal, Jawan, RRR![submenu-img]() IPL 2024: DC thrash GT by 6 wickets as bowlers dominate in Ahmedabad
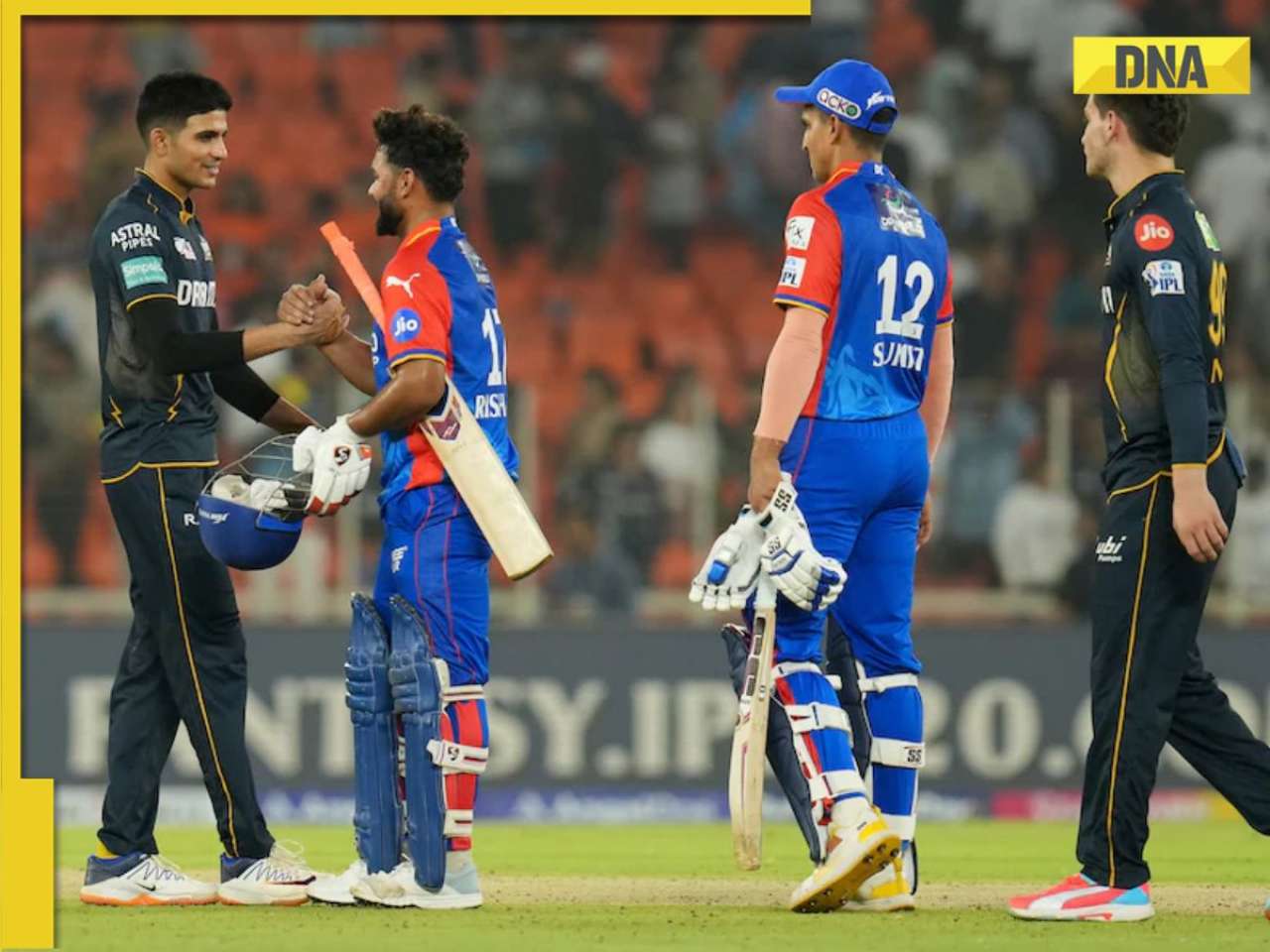
IPL 2024: DC thrash GT by 6 wickets as bowlers dominate in Ahmedabad![submenu-img]() MI vs PBKS, IPL 2024: Predicted playing XI, live streaming details, weather and pitch report
MI vs PBKS, IPL 2024: Predicted playing XI, live streaming details, weather and pitch report![submenu-img]() MI vs PBKS IPL 2024 Dream11 prediction: Fantasy cricket tips for Mumbai Indians vs Punjab Kings
MI vs PBKS IPL 2024 Dream11 prediction: Fantasy cricket tips for Mumbai Indians vs Punjab Kings ![submenu-img]() IPL 2024: Big boost for LSG as star pacer rejoins team, check details
IPL 2024: Big boost for LSG as star pacer rejoins team, check details![submenu-img]() IPL 2024: Jos Buttler's century power RR to 2-wicket win over KKR
IPL 2024: Jos Buttler's century power RR to 2-wicket win over KKR![submenu-img]() This Swiss Alps wedding outshine Mukesh Ambani's son Anant Ambani's Jamnagar pre-wedding gala
This Swiss Alps wedding outshine Mukesh Ambani's son Anant Ambani's Jamnagar pre-wedding gala![submenu-img]() Watch viral video: Deserts around Saudi Arabia's Mecca and Medina are turning green due to…
Watch viral video: Deserts around Saudi Arabia's Mecca and Medina are turning green due to…![submenu-img]() Shocking details about 'Death Valley', one of the world's hottest places
Shocking details about 'Death Valley', one of the world's hottest places![submenu-img]() Aditya Srivastava's first reaction after UPSC CSE 2023 result goes viral, watch video here
Aditya Srivastava's first reaction after UPSC CSE 2023 result goes viral, watch video here![submenu-img]() Watch viral video: Isha Ambani, Shloka Mehta, Anant Ambani spotted at Janhvi Kapoor's home
Watch viral video: Isha Ambani, Shloka Mehta, Anant Ambani spotted at Janhvi Kapoor's home






































)




)
)
)
)
)
)